Have you ever wondered why the sky is blue, or why clouds are white? The answer lies in the fascinating phenomenon of reflection, and more specifically, Earth’s reflection ratio. This invisible dance of light and matter plays a vital role in our planet’s energy balance, climate, and even the beauty we see each day.
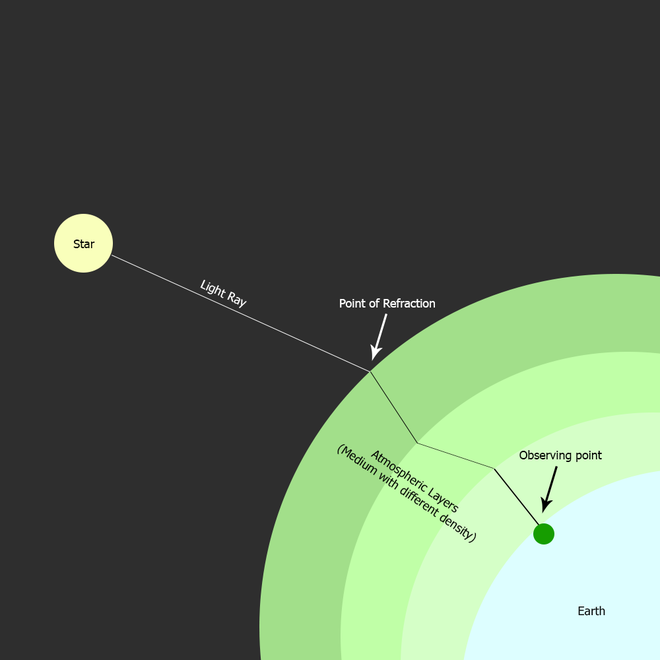
Image: barcelonageeks.com
Earth’s reflection ratio, also known as albedo, is a measure of how much sunlight is reflected back into space. This ratio, expressed as a percentage, determines how much of the sun’s energy is absorbed by our planet and how much is bounced back. Understanding albedo is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of Earth’s climate, since it influences the amount of energy available to drive weather patterns and regulate temperatures.
The Reflective Surface: From Snow to Oceans
The Spectrum of Reflection: From Snow to Oceans
Earth’s surface is a complex tapestry of different materials, each with its own unique reflectivity. Snow and ice, for example, are highly reflective, boasting an albedo of around 80-90%. This means they reflect a large portion of incoming sunlight, contributing to the cooling effect often associated with these icy landscapes. In contrast, dark surfaces like forests and oceans absorb more light, leading to higher temperatures.
This variation in reflectivity across Earth’s surface is a key factor driving regional climate differences. The stark contrast between the bright, reflective polar regions and the dark, absorbing equatorial regions plays a significant role in the global circulation of air and water, influencing weather patterns and ocean currents.
From Clouds to Dust: Atmospheric Albedo
Earth’s atmosphere also plays a crucial role in reflecting sunlight. Clouds, with their wispy white forms, act as excellent reflectors, sending a significant portion of sunlight back into space. The amount of cloud cover can significantly influence regional albedo, particularly in areas prone to heavy cloud formation or periods of cloudless skies.
Atmospheric aerosols, tiny particles suspended in the air, also contribute to albedo. Volcanic eruptions, for instance, release ash and gases into the atmosphere, creating a veil that reflects sunlight, contributing to a cooling effect. Similarly, dust particles from deserts or industrial pollution can influence regional albedo, sometimes leading to local warming or cooling depending on the particle composition and size.
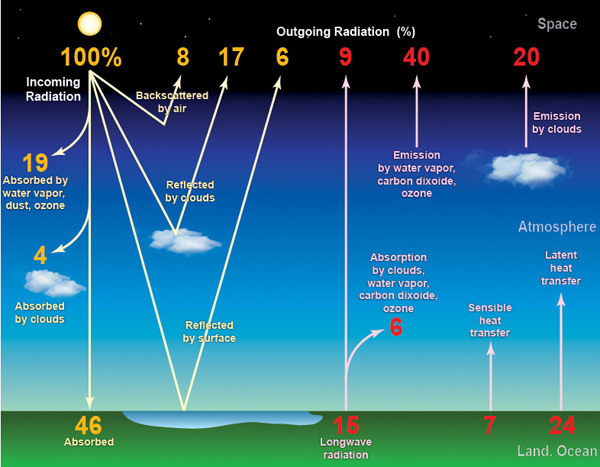
Image: socratic.org
The Role of Albedo in Climate Change
Albedo is a critical factor in understanding and predicting climate change. As the Earth’s surface and atmosphere undergo changes, their reflectivity is altered, impacting the energy balance and ultimately affecting global temperatures.
For instance, the melting of glaciers and ice caps, driven by rising global temperatures, reduces Earth’s overall reflectivity. This loss of reflective surface allows more sunlight to be absorbed, contributing to further warming. This feedback loop, where warming leads to less reflection, creating even more warming, is a major concern in climate science.
Deforestation, with its replacement of reflective forests with darker agricultural lands, also contributes to changes in albedo. This process leads to a net increase in the absorption of solar energy, further amplifying the warming effect.
The Future of Albedo: Understanding and Managing Change
The evolving albedo of our planet is a complex and dynamic phenomenon. Understanding it is crucial for developing effective climate change mitigation strategies. Research into albedo is crucial for making informed decisions about land management, particularly in areas sensitive to climate change, like Arctic regions.
From Satellites to Models: Studying Albedo
Scientists use various methods to monitor and study Earth’s albedo. Satellites equipped with specialized instruments measure the amount of reflected sunlight from different areas of the planet. These measurements provide valuable insights into regional and global albedo variations, helping researchers understand the drivers of change and their potential impact on climate.
Climate models, complex computer simulations of Earth’s climate system, incorporate albedo data to predict future climate scenarios. By simulating the effects of various factors, such as changes in land use, greenhouse gas emissions, and volcanic activity, models can provide valuable insights into the potential impacts of albedo changes on global temperatures and weather patterns.
Reflection Ratio For Earth’S Atmosphere Or Surface
The Reflection of Our Actions: A Call to Action
The reflection ratio of our planet is not just a scientific concept; it reflects our collective impact on Earth’s climate. Our decisions regarding land use, energy production, and environmental practices directly influence the albedo of our planet, shaping the future of our climate.
As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, understanding and managing albedo becomes increasingly important. By promoting sustainable practices, reducing deforestation, and investing in clean energy sources, we can help maintain a healthy reflectivity for our planet, ensuring a brighter and more sustainable future.






