I remember vividly the day my art teacher first introduced the concept of subtractive color. We were experimenting with mixing paints, and I was trying to understand why combining blue and yellow didn’t create a vibrant green, as I had intuitively expected. Instead, it produced a muddy, murky shade. My teacher patiently explained the difference between subtractive and additive color mixing, and it opened my eyes to a whole new world of color theory. This revelation sparked my curiosity, and I delved deeper into the fascinating world of color mixing, eager to unravel the secrets behind this seemingly counterintuitive phenomenon.

Image: www.slideserve.com
The concept of subtractive color mixing is both intriguing and essential to understanding color theory. It governs how we perceive color when working with pigments, dyes, or inks, rather than light. By understanding the principles of subtractive color mixing, artists, designers, and even everyday individuals can create captivating and nuanced color schemes for their artwork, projects, and even their personal style.
Unveiling the Mystery of Subtractive Color
Subtractive color mixing, in essence, refers to the process of creating new colors by mixing pigments. When pigments are combined, they absorb specific wavelengths of light and reflect others, leading to the perception of a different color. As pigments are added, more light gets absorbed, resulting in darker and more muted colors.
This process stands in contrast to additive color mixing, which involves combining light sources. In additive color mixing, the addition of colors leads to brighter and brighter hues, eventually culminating in white light. Think of a spotlight shining on a stage. The mixing of red, green, and blue light results in white light, while combining any two of these primaries creates a secondary color—yellow, cyan, or magenta.
Understanding the Primary Colors of Subtractive Color Mixing
The foundation of subtractive color mixing rests upon the three primary colors: cyan, magenta, and yellow. These primary colors, when mixed in various combinations, create a diverse array of secondary and tertiary colors. By combining any two primary colors, you generate a secondary color: cyan + magenta = blue, magenta + yellow = red, and cyan + yellow = green.
The secondary colors can then be mixed with neighboring primary colors to create tertiary colors, resulting in even more diverse hues. For example, mixing blue (cyan + magenta) with cyan creates a teal color, while mixing blue with magenta produces a purple hue.
The Role of Black and White
While not strictly considered primary colors in subtractive color mixing, black and white play crucial roles in achieving specific color effects. Black, often referred to as a “color reducer,” is used to darken and desaturate hues. White, conversely, acts as a “color reducer,” diluting pigments and creating lighter shades.
Understanding how these colors work in subtractive color mixing allows artists to create vibrant and nuanced color palettes, incorporating both light and dark tones, as well as variations in saturation. It opens the door to endless creative possibilities, enabling artists to express their individuality and capture the essence of their artistic vision.
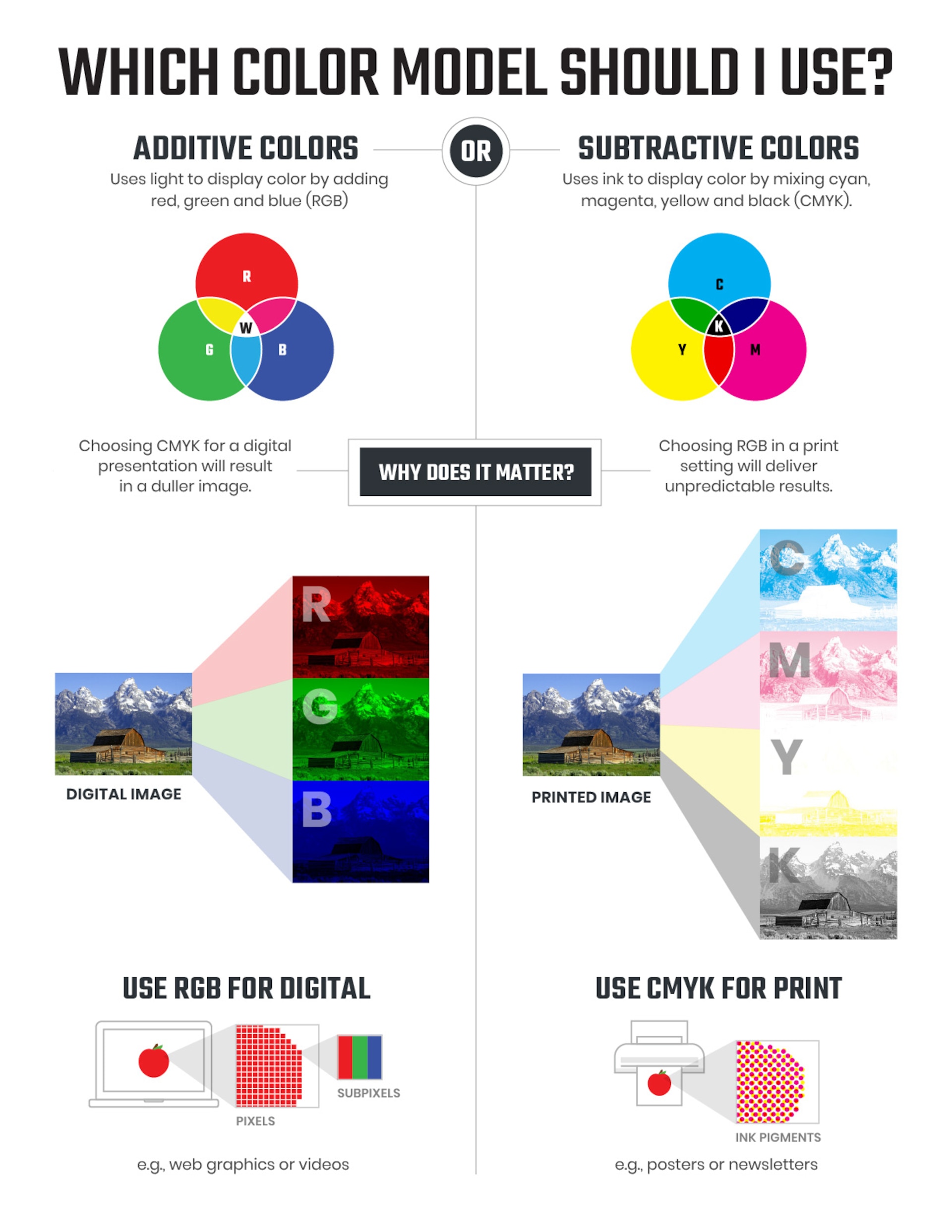
Image: discuss.codecademy.com
Examples of Subtractive Color
Subtractive color is all around us, influencing the colors we see in everyday objects, paintings, and even the natural world. Here are some examples of subtractive color in action:
1. Painting
Painting is a quintessential example of subtractive color mixing. Artists utilize pigments, such as acrylics, oils, or watercolors, to create their artwork. By combining these pigments on a canvas, they mix different colors, absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting others, ultimately achieving a specific color palette.
2. Printing
Printing processes, like offset printing or digital printing, also rely heavily on subtractive color mixing. In these processes, inks based on cyan, magenta, and yellow are used, along with black for deeper shades, to replicate images and text on paper. This process, known as CMYK color, represents the foundation of modern printing technology, responsible for producing the vibrant colors we see in magazines, newspapers, and other printed materials.
3. Dyeing
Dyeing fabrics, clothes, or yarn is another example of subtractive color mixing. Dyes work by staining fibers with pigments, resulting in colored materials. The process involves combining different dyestuffs to achieve desired shades, producing a wide array of colors for textiles and other decorative fabrics.
The Latest Trends in Subtractive Color
The world of color is constantly evolving, with new trends and techniques emerging in various disciplines. In the realm of design, subtractive color continues to be a vital element in achieving specific visual effects and conveying desired emotions.
One emerging trend is the increasing popularity of monochromatic color palettes. These palettes rely on various shades of a single color, often utilizing the subtractive color mixing principles to achieve subtle variations in tone and saturation. Monochromatic palettes often generate a sense of sophistication, elegance, and simplicity, making them popular for contemporary design projects.
Expert Tips for Mastering Subtractive Color
As an art enthusiast who has spent years experimenting with subtractive color, I’ve learned a few essential tips that can help you create stunning color combinations:
- Understand the Color Wheel: The color wheel is an invaluable tool for understanding the relationship between colors and how they interact when mixed. Use it to identify complementary colors, which create strong contrast and vibrancy, and analogous colors, which provide a more subtle and harmonious palette.
- Start with a Light Touch: When mixing pigments, gradually add colors to avoid overwhelming the base color. A light touch ensures a more controlled and nuanced mixing process, allowing for more precise color adjustment.
- Experiment with Color Combinations: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different color combinations, breaking away from conventional rules. Exploring unexpected pairings can lead to exciting discoveries and unique color palettes that reflect your individual style.
- Use White and Black Sparingly: While white and black can be valuable tools in subtractive color mixing, use them sparingly. Excessive use of black can lead to muddy colors, while too much white can dilute the vibrancy of the palette.
- Observe Nature: Nature is a boundless source of inspiration for color combinations. Observe the colors of flowers, the sky, or the changing leaves—they offer endless possibilities for creating harmonious and captivating color palettes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between subtractive and additive color mixing?
A: Subtractive color mixing involves mixing pigments, which absorb wavelengths of light and reflect others. Additive color mixing, on the other hand, combines light sources, with each light source adding its color to the mix.
Q: Why do some colors appear different under different lighting conditions?
A: Lighting conditions significantly affect how we perceive color. Light sources emit different wavelengths of light, influencing the wavelengths that pigments absorb and reflect. This phenomenon explains why a dress may appear a different color in daylight compared to artificial light.
Q: What are some practical applications of subtractive color mixing?
A: Subtractive color mixing is essential in numerous fields, including painting, printing, dyeing, and even food coloring. It is a fundamental principle behind the creation of captivating colors in our everyday life.
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Subtractive Color
Conclusion
Subtractive color mixing is a fascinating and essential concept for understanding how we perceive color in the world around us. By learning the principles of subtractive color mixing, artists, designers, and individuals alike can create exciting and nuanced color palettes. From mixing pigments on a canvas to creating vibrant prints, this process offers endless potential for artistic expression and creativity.
Are you interested in learning more about subtractive color mixing? What questions do you have about this topic?






