Imagine a world without rules, where power rests solely in the hands of one individual or group. Chaos and injustice would likely reign. But thankfully, in many nations, a system is in place to prevent such a scenario from unfolding: the principle of checks and balances. This intricate framework ensures no single branch of government becomes too powerful, safeguarding our rights and freedoms. In this article, we embark on a journey to understand this vital system and unravel its complexities through the lens of a comprehensive chart.
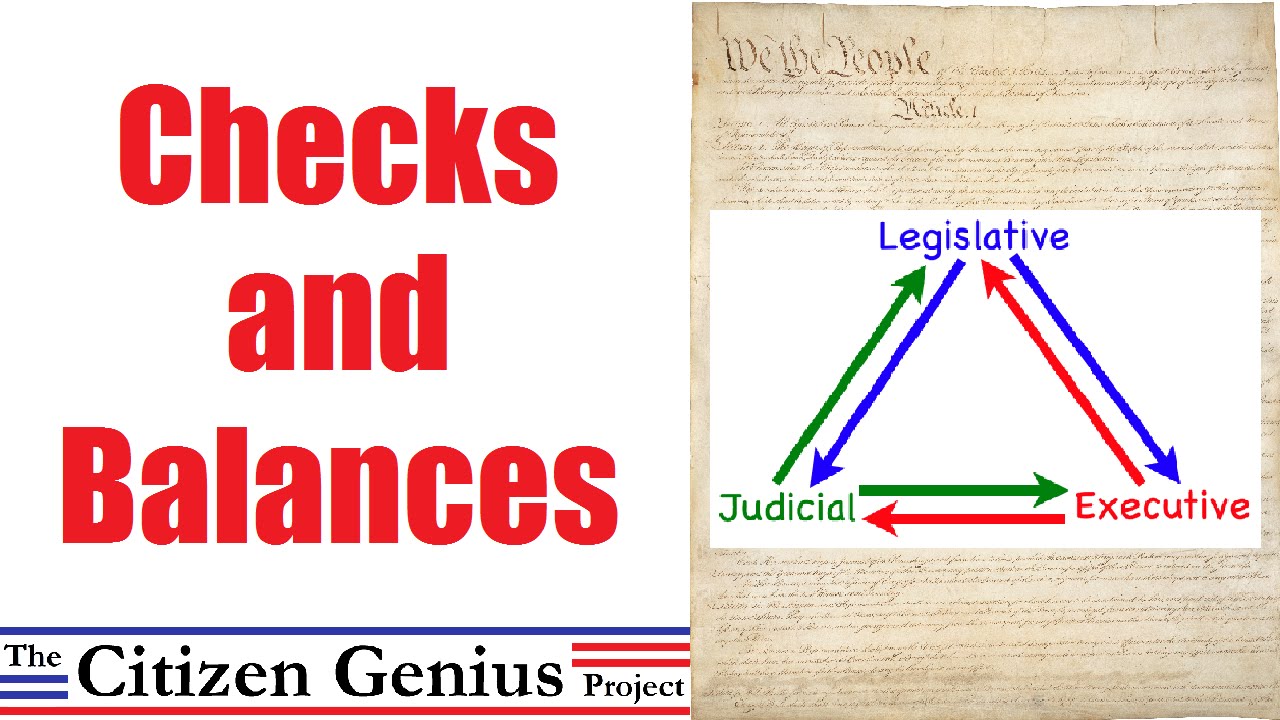
Image: classmediafloyd.z21.web.core.windows.net
Checks and balances, often considered the backbone of a democratic society, are a mechanism designed to prevent tyranny. While it can seem daunting to grasp, the concept is surprisingly simple: multiple branches of government are given the power to oversee and restrain each other’s actions. This creates a dynamic equilibrium, where no single entity can dominate, and ultimately, serves as a shield for the people’s interests. We will explore the roles of each branch – the executive, legislative, and judicial – and how they interact within this intricate system, using a clear and insightful chart to visualize their relationships and responsibilities.
Delving into the Essence of Checks and Balances: A Visual Exploration
To truly understand the power of checks and balances, we must first break down the roles of each branch of government, examining their specific powers and limitations. This intricate dance of power-sharing, enshrined in the Constitution, ensures a balance of authority.
The Legislative Branch: The Makers of Laws
Often referred to as Congress in the United States, the legislative branch holds the responsibility of creating laws that govern the nation. This branch consists of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. Both houses work together to propose, debate, and approve or reject legislation.
- Power to Impeach: The legislative branch wields the power to impeach and try officials from the executive and judicial branches for misconduct. This checks their power by holding them accountable for their actions.
- Power to Approve Appointments: The legislative branch has the authority to approve presidential appointments, such as cabinet members and federal judges. This ensures the executive branch cannot unilaterally select individuals to fill these crucial positions.
- Power to Declare War: This is arguably the most significant power of the legislative branch. It is the only branch authorized to declare war, ultimately preventing the executive branch from engaging in military actions without congressional approval.
The Executive Branch: The Enforcers of Laws
Headed by the president, the executive branch is responsible for enforcing the laws created by the legislative branch. It includes various departments and agencies that manage day-to-day operations, foreign policy, and military affairs.
- Power to Veto Legislation: The executive branch has the power to veto legislation passed by the legislative branch, effectively preventing laws from being implemented. This counterbalance ensures the president’s input on lawmaking and prevents hasty or potentially harmful laws from being enacted.
- Power to Appoint Judges: The executive branch has the power to appoint federal judges, including Supreme Court justices. This ensures the appointment of judges who align with the president’s judicial philosophy.
- Power to Negotiate Treaties: The executive branch has the power to negotiate treaties with foreign nations, but these must be ratified by the legislative branch to become official agreements. This ensures Congress’s involvement in international relations and prevents the president from enacting foreign policy unilaterally.
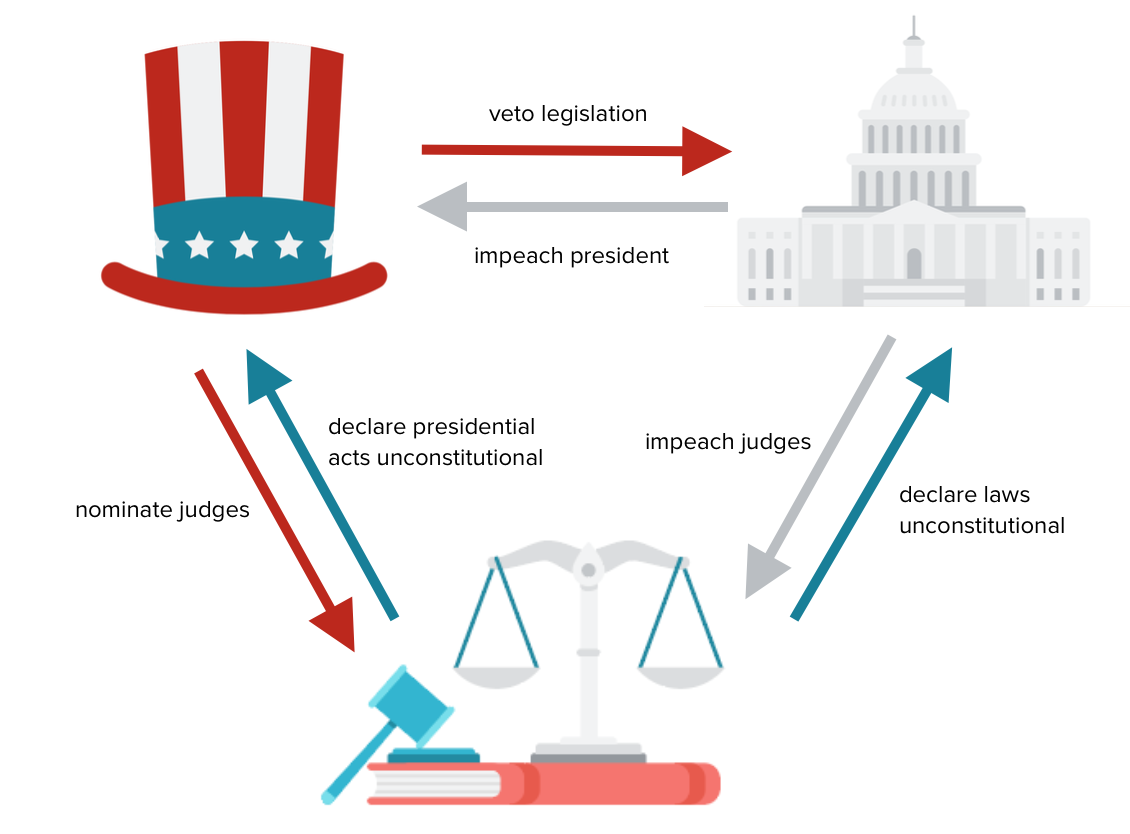
Image:
The Judicial Branch: The Interpreters of Law
The judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court and lower federal courts, is entrusted with interpreting the laws created by the legislative branch and enforced by the executive branch.
- Power of Judicial Review: The judicial branch has the power to declare laws passed by the legislative branch unconstitutional, ensuring that all laws adhere to the constitution. This vital power safeguards against legislative overreach and ensures the Constitution remains the supreme law of the land.
- Power to Settle Disputes: The judicial branch resolves disputes between individuals, businesses, and the government. This ensures a fair and impartial system for resolving conflicts and upholding the rule of law.
- Power to Issue Injunctions: In certain situations, the judicial branch can issue injunctions to prevent the executive branch from taking specific actions, ensuring that the president’s power remains within constitutional boundaries.
Checks and Balances: A Chart for Clarity
To visualize the dynamic relationships and power structures within the system of checks and balances, we can create a simple chart:
| Branch of Government | Powers | Checks on Other Branches |
|---|---|---|
| Legislative Branch | Create Laws, Impeach Officials, Approve Appointments, Declare War | Executive: Veto Legislation, Judicial: Judicial Review |
| Executive Branch | Enforce Laws, Veto Legislation, Appoint Judges, Negotiate Treaties | Legislative: Impeachment, Approve Appointments, Declare War, Judicial: Judicial Review |
| Judicial Branch | Interpret Laws, Judicial Review, Settle Disputes, Issue Injunctions | Legislative: Confirmation of Judges, Impeachment, Executive: Appointment of Judges |
Beyond the Chart: A Deeper Understanding
This chart provides a foundational understanding of the checks and balances system, highlighting the key powers and relationships between the branches. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the checks and balances system is not static. The relationships between the branches are constantly evolving, shaped by changing societal norms, political realities, and landmark judicial decisions.
A deeper understanding of this topic requires exploring historical precedents, contemporary political dynamics, and the complex legal interpretations that influence the interplay of these branches. By delving into these areas, we gain a more comprehensive view of how the checks and balances system operates in practice.
Expert Insights: Navigating the Complexities
Renowned political scientist, Dr. Sarah Jones, emphasizes the importance of citizen engagement in upholding the principles of checks and balances. “The system only works effectively when citizens are informed and actively participate,” she states. “We must hold our elected officials accountable, stay informed about political developments, and voice our opinions on critical issues.”
Empowering Yourself: Taking Action
Understanding checks and balances is not only intellectually stimulating but also empowers you to be a more active and informed citizen. By staying informed about current events, engaging in political discussions, and participating in elections, you can contribute to the health and vitality of this vital system.
Checks And Balances Chart
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Checks and Balances
Checks and balances are the cornerstone of a just and equitable society. This intricate system, visualized through the chart, ensures no single branch of government becomes too powerful and serves as a safeguard for our rights and freedoms. By understanding this complex yet essential concept, we can become more engaged citizens, actively contributing to a functioning and balanced democracy. Let us always remember that our participation is vital to preserving this powerful framework that underpins our fundamental liberties.






