Ever stepped outside on a crisp autumn day, checked the thermometer, and seen a reading of 39 degrees Fahrenheit? Perhaps you’re planning a trip to a place where the weather is described in Celsius but you’re more familiar with Fahrenheit. Have you ever wondered what 39 degrees Fahrenheit translates to in the metric system? Understanding the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is crucial, especially as globalization brings people and information together from diverse corners of the world.
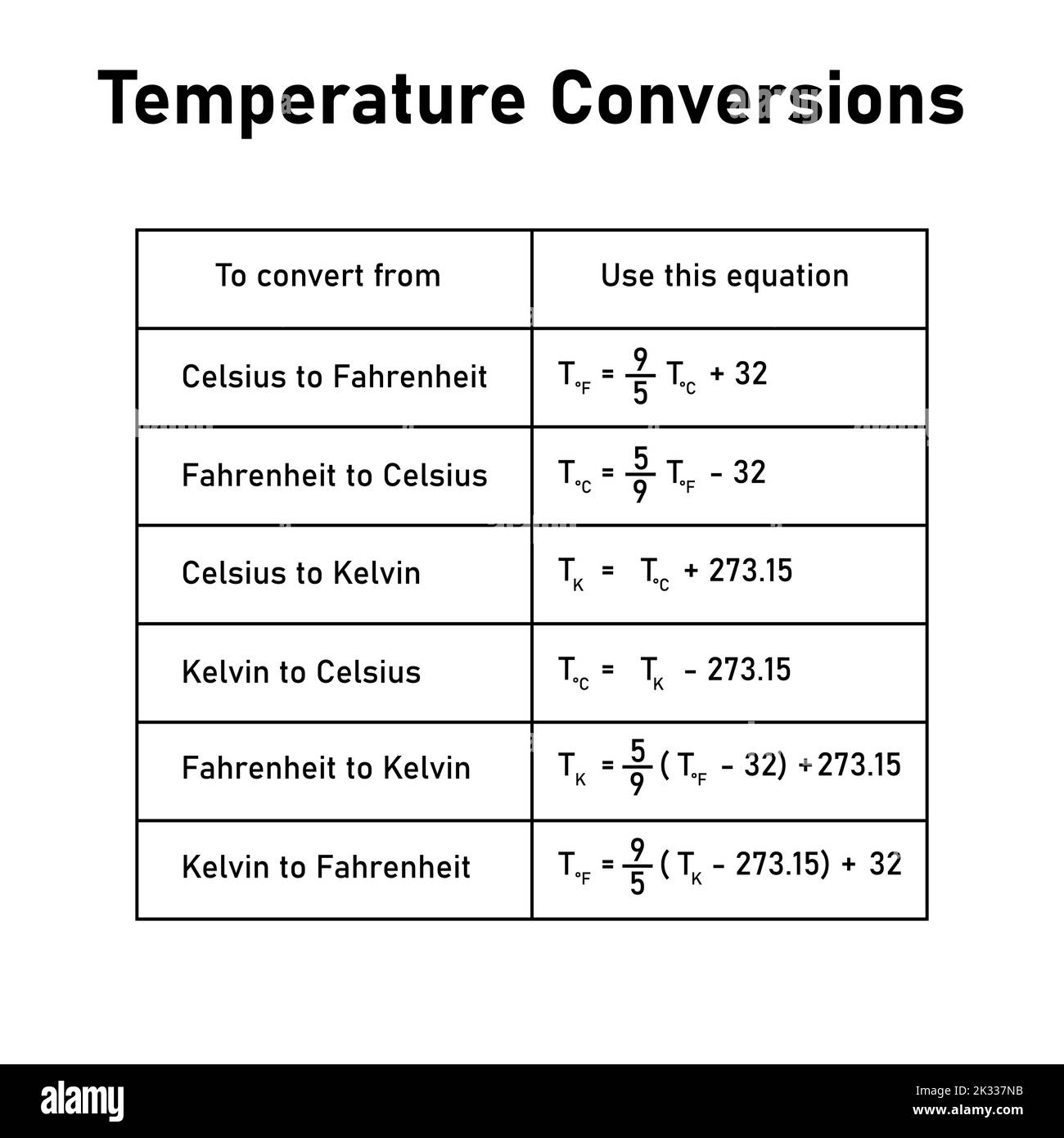
Image: www.alamy.es
This article delves into the world of temperature conversion, specifically focusing on converting 39 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius. We’ll explore the historical context behind these scales, discuss the formula used for conversion, and highlight the practical applications of understanding this conversion in everyday life. We’ll also delve into the nuances of temperature measurement and its impact on various aspects of our world, from weather forecasting to cooking and even our own personal comfort.
The Tale of Two Scales: Fahrenheit vs. Celsius
Fahrenheit: A Tale of Wine and Salt
The Fahrenheit scale, named after German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, emerged in the early 18th century. Fahrenheit’s initial scale used a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride (a salt) as reference points, leading to a rather peculiar starting point of 0 degrees. He redefined his scale using the freezing point of water (32 degrees F) and the boiling point of water (212 degrees F) as his benchmarks. This scale gained popularity throughout Europe and later spread to the Americas, becoming the dominant system in the United States.
Celsius: A System Based on Water
In contrast, the Celsius scale, named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, emerged in the 18th century based on two key points: the freezing point of water (0 degrees C) and the boiling point of water (100 degrees C). The simplicity and logical framework of the Celsius scale – where 0 represents freezing and 100 represents boiling – made it more intuitive and easier to work with. Today, the Celsius scale is the standard measure of temperature used in the majority of countries globally, including those in Europe, Asia, Africa, and South America.
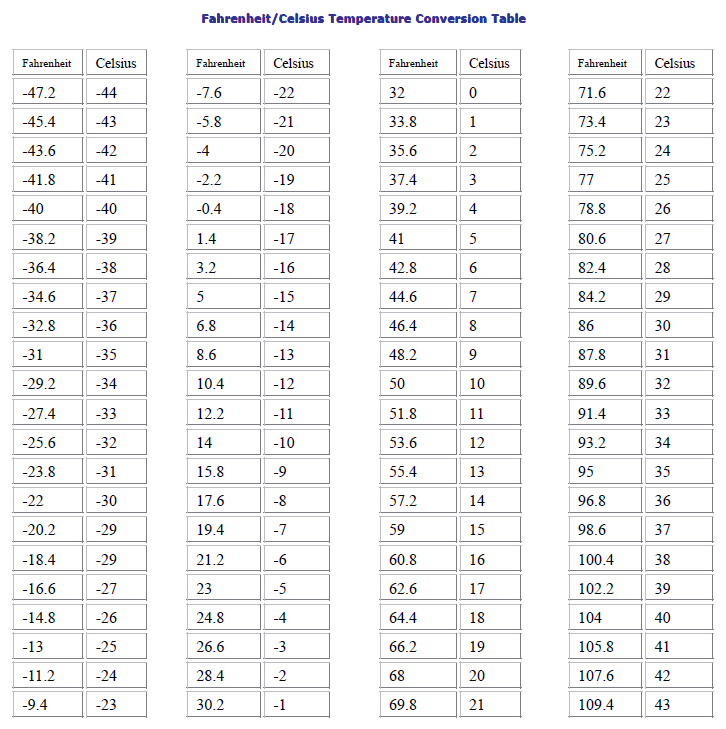
Image: brooklynmyles.blogspot.com
39 Fahrenheit to Celsius: The Conversion
Now, the moment you’ve been waiting for: converting 39 degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius. Thankfully, there’s a simple formula that takes care of this conversion:
°C = (°F – 32) * 5/9
Let’s apply this to our 39 degrees Fahrenheit:
(39°F – 32) * 5/9 = 7 * 5/9 = 3.89°C
Therefore, 39 degrees Fahrenheit is equivalent to approximately 3.89 degrees Celsius.
Understanding the Significance of the Conversion
Knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential for several reasons:
Travel
Imagine you’re planning a vacation to a country that primarily uses the Celsius scale. If the weather forecast predicts a high of 15 degrees Celsius, would you be prepared for a warm day or a chilly one? By converting this to Fahrenheit (15°C * 9/5 + 32 = 59°F), you’d know to pack accordingly for a comfortable temperature.
Medical Monitoring
In the medical world, body temperature is often monitored using both Fahrenheit and Celsius. Knowing how to convert these values is crucial for accurate medical diagnosis and treatment.
Cooking
Many recipes use temperature measurements in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Converting between the two scales ensures you cook meals perfectly by adhering to the correct temperature settings.
Beyond the Basics: The Nuances of Temperature Measurement
Absolute Zero: The Theoretical Minimum
The fascinating world of temperature extends beyond simple conversions. In the realm of physics, the concept of absolute zero, which equates to -273.15 degrees Celsius or -459.67 degrees Fahrenheit, represents the lowest possible temperature. This is the point where all molecular motion theoretically stops. While reaching absolute zero is practically impossible, understanding this theoretical limit helps us understand the nature of heat and energy.
Beyond The Scale: The Kelvin Scale
Another important scale in the world of temperature measurement is the Kelvin scale. The Kelvin scale, unlike the Fahrenheit and Celsius scales, is an absolute scale. The starting point of 0 Kelvin (K) corresponds to absolute zero. Each Kelvin degree is equal to one Celsius degree. This means that 39 degrees Celsius is equal to 312.15 Kelvin (39°C + 273.15 = 312.15 K).
The Impact of Temperature: From Weather to Weather
The Influence of Temperature on Weather
Temperature plays a pivotal role in determining weather patterns and climate. Differences in temperature across the globe drive atmospheric circulation, influencing wind patterns and precipitation. Temperature fluctuations impact the severity and duration of seasons, impacting agriculture, wildlife, and human activity.
The Impact of Temperature on Our Bodies
Our bodies thrive within a narrow temperature range. Our core body temperature needs to remain around 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius) for optimal function. Fluctuations in body temperature can signal illness, prompting the immune system to respond. Temperature extremes can pose health risks, leading to dehydration, heat stroke, or hypothermia.
39 Fahrenheit To Celsius
Conclusion
Understanding the conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a valuable skill that transcends basic calculations. It allows us to navigate a world where temperature is measured in both systems, making it possible to interpret weather forecasts, prepare meals, and ensure our well-being. Exploring the history and nuances of temperature measurement further deepens our appreciation for this fundamental aspect of our physical world. Whether you’re a traveler venturing to new destinations, a chef perfecting your culinary creations, or simply curious about the world around you, embracing the ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius opens doors to a deeper understanding of our environment and ourselves. So, the next time you encounter a temperature reading in one system or the other, remember the simple conversion formula, and you’ll be ready to navigate the world of temperature with ease and confidence!






