Imagine a world where everyone – regardless of gender – has equal opportunities, equal rights, and an equal voice. This vision, a world free from the shackles of gender inequality, is the driving force behind feminist theory. But what exactly is feminist theory, and how does it impact our understanding of the world around us? Let’s embark on a journey to understand the profound impact of this impactful framework within the field of sociology.

Image: helpfulprofessor.com
Feminist theory is more than just a lens; it is a powerful tool that illuminates the intricate web of power dynamics woven through society. It invites us to question the deeply ingrained gender norms and inequalities that we often perceive as natural, showing us that these are not biological inevitabilities, but rather social constructs shaped by historical and cultural forces. Understanding feminist theory allows us to challenge the status quo and envision a more equitable future.
A Tapestry of Perspectives: The Many Faces of Feminist Theory
The beauty of feminist theory lies in its diversity. It is not a monolithic concept but rather a multifaceted framework encompassing a wide range of perspectives. To grasp its essence, it is essential to understand its various strands:
- Liberal Feminism: Emphasizing individual rights and equality for women, this stream advocates for legal and political reforms to dismantle systemic inequalities. Imagine a world where women can access education, healthcare, and economic opportunities on par with men.
- Radical Feminism: This perspective calls for a more radical transformation, believing that the root of gender inequality lies in patriarchal systems themselves. It envisions a dismantling of traditional gender roles and power structures, paving the way for a world where women are not obligated to conform to societal expectations.
- Socialist Feminism: This branch intertwines feminism with socialist ideals, underscoring the impact of capitalism and class structures on women’s oppression. It seeks to dismantle the exploitative systems that perpetuate gender inequality and economic exploitation.
- Black Feminism: This powerful voice within feminist theory sheds light on the unique experiences of Black women, exploring the intersections of race, gender, and class. It highlights the systemic oppression faced by Black women, advocating for the recognition and dismantling of these complex disparities.
- Postmodern Feminism: This perspective challenges traditional notions of gender and identity, emphasizing the fluidity and diversity of individual experiences. It dismantles the binary structures of “male” and “female” and embraces the complexities of gender expression.
The Untangling of Societal Knots: Feminist Theory and its Impact on Sociology
Feminist theory has revolutionized the field of sociology, pushing the discipline to question long-held assumptions and analyze social phenomena through a gendered lens. Here are some of its key contributions:
- The Reframing of Family Structures: Feminist theory has revolutionized our understanding of the family, highlighting the patriarchal dynamics that shape family relationships, including gender roles, division of labor, and power imbalances. It challenges the traditional nuclear family model, recognizing the diverse forms that families take and the inequalities that can exist within them.
- The Gendered Nature of Work and the Workplace: Feminist theory has brought to light the gendered nature of the workplace. It explores the ways in which women are often relegated to lower-paying jobs, face gender-based discrimination and harassment, and are excluded from leadership positions.
- The Construction of Gender Identities: Feminist theory has deconstructed the binary notions of “masculine” and “feminine”. It delves into the complex social construction of gender roles, exploring how cultural norms and expectations shape individuals’ identities and experiences.
- The Intersectionality of Gender with Other Social Factors: Feminist theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of gender with other social categories like race, class, and sexual orientation. It recognizes that women’s experiences are shaped by a complex interplay of these factors, leading to diverse forms of oppression.
Feminist Theory in Action: Making the World a More Equitable Place
Feminist theory is not just an academic discourse; it is a call to action. It empowers us to challenge inequalities and advocate for a more just world. Here are some practical ways to apply feminist theory in your everyday life:
- Challenge Gender Stereotypes: Be mindful of ingrained stereotypes that you may encounter, whether in media, personal interactions, or everyday language. Question assumptions and call out harmful gender norms.
- Advocate for Equal Opportunities: Support policies and initiatives that promote equal access to education, employment, healthcare, and political representation for all genders.
- Embrace Inclusive Language: Use inclusive language that recognizes and celebrates diversity in gender expression and identity.
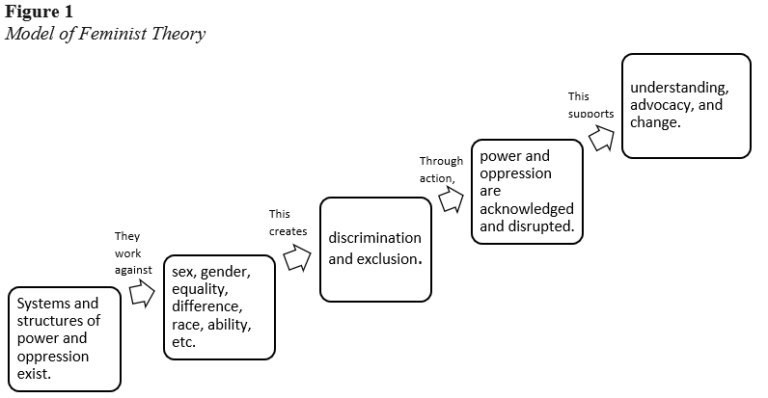
Image: opentext.wsu.edu
What Is The Feminist Theory In Sociology
The Feminist Journey Continues: A World of Endless Potential
Feminist theory is an ongoing conversation. It’s a continual process of questioning, challenging, and evolving, pushing us to strive for a more equitable future. Its significance lies not only in its ability to reveal and challenge injustice, but also in its potential to inspire individual and collective action, leading us toward a world where all genders are valued, empowered, and truly equal.






