Imagine a world where everyone commutes in driverless electric cars, powered by renewable energy. Picture a society where healthcare is free and accessible to all, supported by a system of universal basic income. These visions, radical as they may seem, are the products of social imagination – the ability to envision and conceptualize alternative social structures, systems, and possibilities. It’s a powerful mental tool that transcends the boundaries of the present, challenging us to question the status quo and imagine a better future.

Image: www.slideserve.com
Social imagination is not merely about dreaming up utopian scenarios; it’s about critically analyzing existing social realities and envisioning alternative pathways. It’s the spark that fuels social progress, sparking movements, and shaping policies. In this article, we will delve into the depths of social imagination, exploring its historical roots, key principles, real-world applications, and its profound impact on shaping a more just and equitable world.
Unveiling the Roots of Social Imagination
The concept of social imagination has deep roots in philosophical and sociological thought. While the term itself may be relatively recent, the underlying principles have been explored by thinkers throughout history.
The Seeds of Change: Early Thinkers
Philosophers like Plato and Aristotle grappled with the ideal forms of society and governance. In his “Republic,” Plato envisioned a utopian city-state ruled by philosopher kings, a vision that, despite its flaws, reflected a yearning for a better social order. The Enlightenment thinkers, particularly Jean-Jacques Rousseau, challenged established power structures and advocated for individual freedoms, laying the groundwork for modern democratic ideals.
Early 20th Century: Breaking the Mold
The early 20th century saw a surge of social imagination, fueled by rapid industrialization and social unrest. In “The Condition of the Working Class in England” (1845), Friedrich Engels provided a stark depiction of the exploitative conditions faced by factory workers, sparking a movement for social reform. Karl Marx, with his analysis of capitalism and his vision of a classless society, further ignited imaginations by offering a radical alternative to the prevailing social order.
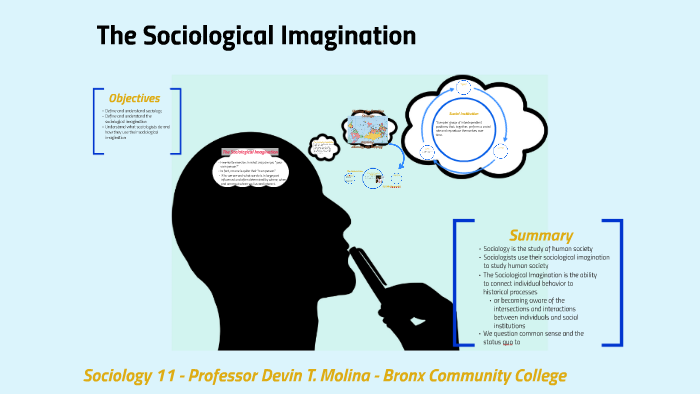
Image: prezi.com
Modern Interpretations: Shaping the Landscape
The concept of social imagination was further developed by sociologists in the mid-20th century. C. Wright Mills, in his seminal work “The Sociological Imagination” (1959), highlighted the importance of connecting personal troubles to broader social issues. He argued that individuals must be able to step outside their immediate experiences and understand the social forces shaping their lives. This ability to transcend personal limitations and see the world through a wider lens is crucial for fostering social imagination.
The Building Blocks of Social Imagination
Social imagination is not simply a haphazard exercise of fantasizing about a better world. It operates within a framework of critical thinking, ethical considerations, and a deep understanding of social dynamics.
Critical Thinking: Questioning the Status Quo
Social imagination starts with questioning the taken-for-granted assumptions and norms that underpin our society. It involves asking: Why are things the way they are? What are the underlying power dynamics? What are the consequences of these structures? This critical questioning allows us to identify limitations and imagine alternative possibilities.
Ethical Compass: Moral Vision and Social Justice
At its core, social imagination is driven by a desire for a more just and equitable world. It aligns with ethical principles like equality, fairness, and human rights. It seeks to address social inequalities, alleviate suffering, and create a society where everyone has opportunities to thrive. This ethical foundation guides the creation of alternative visions and inspires action to bring those visions to life.
Understanding Social Dynamics: Interconnectivity and Complexity
Social imagination requires a deep understanding of how society functions – the interconnectedness of social institutions, the interplay of economic, political, and cultural forces, and the impact of historical trajectories. It involves recognizing the complexities and contradictions within social structures, understanding the root causes of social problems, and identifying levers for change.
Fueling Social Change: Real-World Applications of Social Imagination
Social imagination isn’t just a theoretical construct; it is a potent force for social change, finding expression in various forms across the globe.
From Utopia to Action: Social Movements
Social movements, driven by a collective vision of a better society, are powerful examples of social imagination in action. The Civil Rights Movement, for instance, was fueled by a powerful social imagination that envisioned a world free from racial segregation and discrimination. The movement’s leaders, like Martin Luther King Jr., articulated a vision of an integrated and equal society, inspiring millions to join the fight for justice.
Shaping Policy: Influencing Legislation and Governance
Social imagination also influences policy-making and governance. Policy proposals advocating for universal healthcare, climate action, affordable housing, and other social programs are born out of a vision for a more just and sustainable society. These proposals often stem from research, activism, and social movements that have successfully used social imagination to reframe public discourse and advocate for change.
Innovation for Social Good: Technological Solutions and Ethical Considerations
In the age of technological advancements, social imagination is increasingly being applied to create innovative solutions to social problems. From using artificial intelligence to fight poverty to developing sustainable energy sources, the potential for social good is substantial. However, it is crucial that technological innovations are guided by ethical considerations, ensuring they do not exacerbate existing inequalities or create new problems.
The Future of Social Imagination: Embracing Collaboration, Diversity, and Interconnectedness
As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, social imagination becomes even more crucial for building a sustainable and equitable future. Key aspects of this evolving landscape include:
Collaborative Imagination: Collective Intelligence and Collective Action
Social imagination is not a solitary pursuit; it thrives through collaboration. Activism, community organizing, and participatory democracy all encourage collective imagination, leveraging the wisdom and experiences of diverse individuals to create more comprehensive and inclusive visions.
Diverse Perspectives: Embracing the Pluralism of Social Imagination
Social imagination benefits from diverse perspectives and experiences. Encouraging dialogue and inclusivity across social groups, cultures, and generations allows for a wider range of visions and solutions to emerge, challenging the limitations of narrow perspectives.
Global Interconnections: Thinking Beyond Borders
In a globalized world, social imagination must extend beyond national boundaries. Recognizing the interconnectedness of human societies is critical for addressing global issues like climate change, poverty, and migration. Collaborative efforts and shared visions are crucial for tackling these challenges and creating a more just and sustainable world for all.
Example Of Social Imagination
Conclusion: Cultivating Social Imagination for a Better Tomorrow
Social imagination is a powerful tool, empowering us to envision a better world and work towards a more just and equitable future. By embracing critical thinking, ethical considerations, and a deep understanding of social dynamics, we can cultivate this vital mental capacity. By engaging in collaborative efforts, seeking diverse perspectives, and recognizing global interconnectedness, we can ensure that social imagination continues to be a driving force for positive change, shaping a brighter future for generations to come. Embrace the power of social imagination and join the movement to build a world that reflects our shared aspirations for a better tomorrow.






