Imagine a world where your opportunities, your access to resources, and even your life expectancy are determined by the family you were born into. This isn’t a dystopian novel; it’s a reality for millions across the globe, shaped by the invisible lines of social stratification. These lines, often unseen but keenly felt, are the social hierarchies that separate individuals and groups based on factors like wealth, power, and prestige. Understanding these layers is not just an academic exercise; it’s a crucial step in dismantling inequality and building a more just and equitable society.
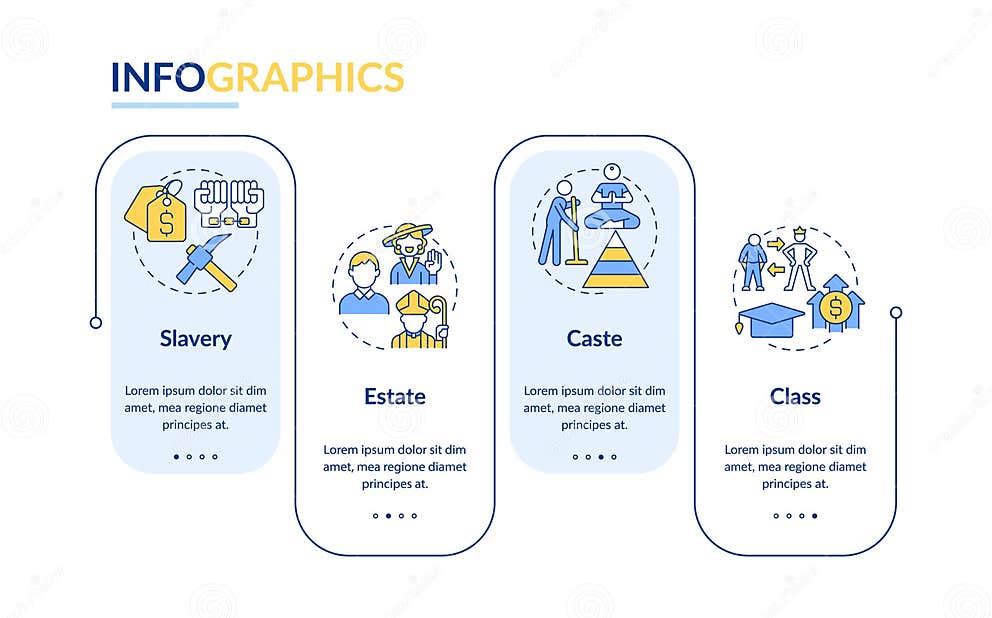
Image: www.dreamstime.com
Social stratification, a term coined by sociologists to describe the uneven distribution of resources and opportunities within a society, is more than just a theoretical concept. It’s a lived experience, shaping our lives in countless ways. From the schools we attend to the jobs we hold to the healthcare we receive, social stratification weaves its way through every aspect of our existence. Recognizing these patterns allows us to understand the complex interplay of power, resources, and social mobility, empowering us to challenge systemic inequalities and advocate for change.
The Layers of Stratification: A Deep Dive into Different Forms
Social stratification manifests in numerous forms, each with its unique characteristics and consequences. Understanding these different types helps us grasp the diverse ways inequality manifests and persists.
1. Caste Systems: The Immutable Order
Imagine a society where your social position is determined at birth and remains fixed for life, with no chance of upward mobility. This is the essence of a caste system, a rigid system of social stratification based on hereditary factors that are often linked to religion or tradition. Rooted in ancient India, caste systems have historically been characterized by strict rules prohibiting intermarriage and social interaction between different groups. These systems are often accompanied by deep-seated prejudices, creating a rigid social hierarchy that perpetuates inequality across generations.
While India has taken significant steps to abolish untouchability and legalize inter-caste marriages, the legacy of caste continues to shape social interactions, access to resources, and political participation in contemporary India. Understanding the historical and ongoing impact of caste systems is crucial for tackling inequality and promoting social justice.
2. Class Systems: The Fluidity of Economic Standing
In contrast to the rigid boundaries of caste systems, class systems offer a degree of social mobility based on economic standing. Class, often defined by factors like income, wealth, education, and occupation, creates social hierarchies where individuals can move between different levels based on their achievements and circumstances. However, the structure of class systems often makes upward mobility challenging, with structural barriers like poverty, lack of access to education, and limited opportunities hindering individuals’ progress.
The concept of class is complex, encompassing economic, social, and cultural dimensions. While some argue that class systems offer a path to upward mobility, others highlight the persistent inequalities embedded within these structures. Understanding the intricacies of class systems is crucial for addressing issues like poverty, wealth inequality, and social mobility.

Image: allforyou.in
3. Estate Systems: The Privileged and the Serfs
Historically, estate systems, often associated with feudal societies, divided society into distinct social groups based on legal and hereditary rights. These systems typically involved a landed aristocracy (the nobility) holding vast estates and enjoying considerable power, supported by a peasantry (serfs) who worked the land in exchange for protection and limited rights.
Estate systems, while largely relegated to the annals of history, illustrate the enduring power of entrenched hierarchies and the influence of legal frameworks in perpetuating inequality. Understanding the historical evolution of estate systems provides insights into the enduring impact of land ownership, political power, and the legacy of feudalism in shaping contemporary societies.
4. Slavery: The Ultimate Form of Inequality
Slavery, a cruel and inhumane system of forced labor, represents the most extreme form of social stratification. Historically practiced across diverse cultures and civilizations, slavery denied individuals their basic human rights, treating them as property without agency or autonomy. The legacy of slavery continues to exert a powerful influence on contemporary societies, impacting issues like race relations, economic disparities, and the persistent fight for equality.
Understanding the historical and ongoing ramifications of slavery is crucial for recognizing the deep-seated inequalities that continue to permeate society. It underscores the importance of acknowledging and addressing the systemic and individual impacts of this abhorrent practice.
Beyond the Layers: The Dynamics of Social Stratification
These are not isolated concepts; they interact and intertwine in complex ways. For instance, caste systems can influence the formation of class structures, with individuals from historically disadvantaged castes often facing limited opportunities despite economic gains. Likewise, the legacy of slavery can shape racial inequalities that intersect with class systems, creating a layered web of oppression.
It’s essential to acknowledge that social stratification often reinforces and perpetuates existing social inequalities. These systems can create a self-perpetuating cycle of disadvantage, where individuals born into lower strata face a steeper uphill battle to achieve upward mobility.
Navigating the Unseen Lines: Empowering Actions for Change
Understanding social stratification is one step, but taking action is another. Here’s how you can empower yourself and make a difference:
1. Become an Informed Citizen: Stay actively informed about the social issues impacting your community and the world, critically engaging with news sources and diverse perspectives.
2. Promote Inclusive Conversations: Encourage open and respectful dialogue about social inequalities within your family, workplace, and social circles, fostering a culture of empathy and understanding.
3. Support Organizations Dedicated to Social Justice: Donate your time or resources to organizations working to dismantle systemic inequalities and advocate for social justice.
4. Advocate for Equitable Policies: Engage with policymakers and elected officials, advocating for policies that address social inequalities and promote inclusive growth.
Types Of Social Stratification
Conclusion: A Call to Action
The lines of social stratification, though often invisible, profoundly shape our lives and our communities. Recognizing these intricate patterns allows us to challenge existing power structures, advocate for a fairer distribution of resources, and ultimately build a society where everyone has a chance to thrive, regardless of their background or social standing. It’s a journey that demands ongoing engagement, empathy, and collective action, a journey we must all undertake together.






