Have you ever stopped to think about how your life might be different if you were born into a different family, or a different part of the world? Imagine if your opportunities were predetermined not by your talent or drive, but by the circumstances of your birth. This is the very essence of ascribed status, a concept central to the study of sociology. While we often associate status with our achievements and choices, ascribed status reveals a deeper layer of social influence that shapes our realities from the moment we enter the world.
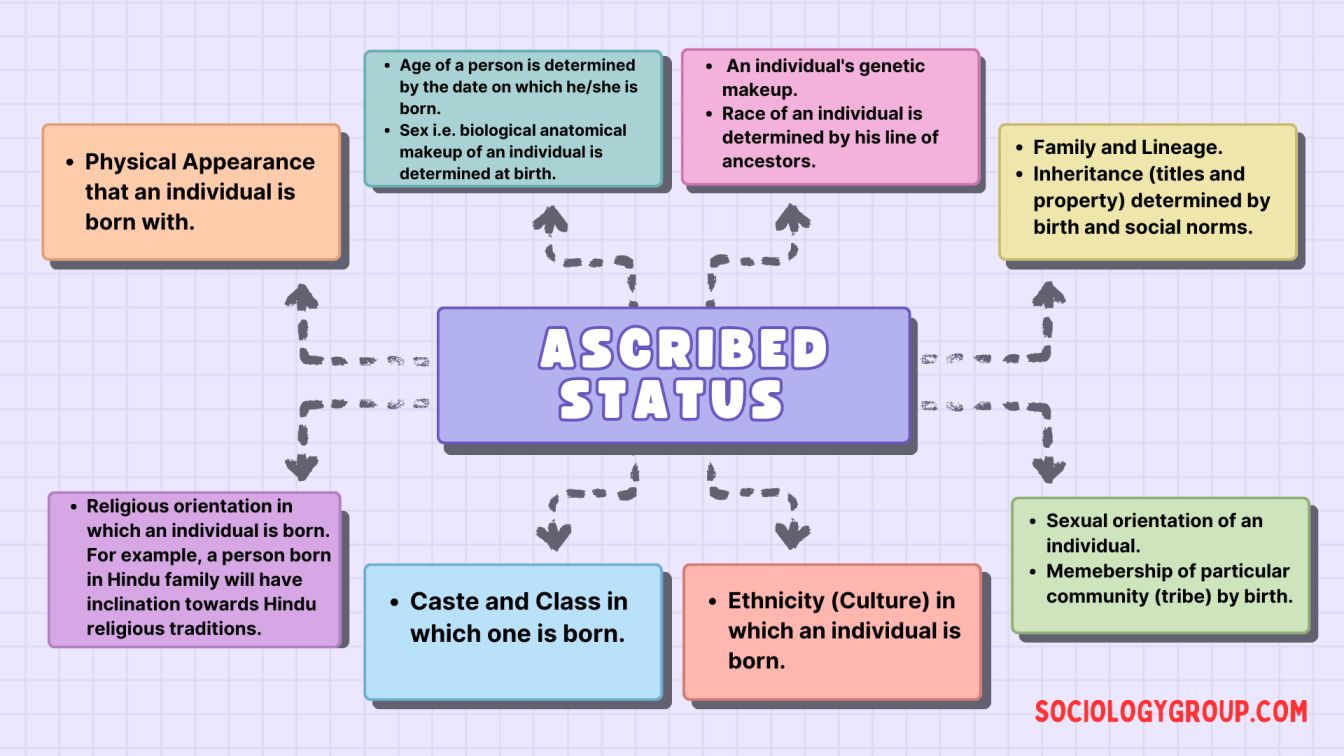
Image: www.sociologygroup.com
Ascribed status refers to the social positions we inherit at birth, determined by factors beyond our control, like race, ethnicity, gender, family background, and even caste in some societies. It’s a powerful force that often dictates our social standing, access to resources, and even the lenses through which others perceive us. Understanding ascribed status is crucial for recognizing systemic inequalities, fostering empathy, and working towards a more equitable society.
The Roots of Ascribed Status
The concept of ascribed status is deeply rooted in the historical foundations of social stratification. From ancient civilizations to modern societies, social hierarchies have existed, often dictated by factors beyond individual merit. In feudal systems, for example, a peasant’s life was predetermined by their birth into a family tied to the land. This system of inherited social standing wasn’t just about power; it was deeply woven into the fabric of daily life, shaping access to resources, education, and even opportunities for social mobility.
While the feudal system may seem like a relic of the past, vestiges of ascribed status persist in various forms even today. Think about the impact of race and ethnicity on someone’s life chances. Individuals may experience discrimination based on their race, limiting their opportunities for employment, housing, or even access to quality healthcare. Gender, too, often serves as an ascribed status, impacting career paths, societal expectations, and even the way people are treated.
The Persistent Impact of Ascribed Status
One of the most significant challenges of ascribed status is its ability to perpetuate inequalities across generations. Children inherit the advantages or disadvantages associated with their parents’ social standings, often leading to a cycle of poverty or privilege. For example, a child born into a family with low socioeconomic status may face limited access to quality education, making it harder to break free from the cycle of poverty.
This isn’t to say that ascribed status determines someone’s entire destiny. Individuals can, and often do, carve out their own paths, defying expectations and achieving remarkable feats despite the challenges they face. However, recognizing the influence of ascribed status is essential for understanding why some individuals face more barriers than others, and why certain groups are more likely to experience systemic disadvantages.
Achieved Status: A Counterpoint to Ascribed Status
In contrast to ascribed status, achieved status refers to the social positions we earn through our efforts, talents, and choices. This includes things like our profession, education level, accomplishments, and even our relationships. Achieved status provides a sense of agency and allows individuals to shape their own destinies.
However, it’s important to remember that ascribed status doesn’t disappear with the advent of achieved status. The influence of our inherited social positions can still shape our opportunities, how we navigate the world, and even how we are perceived by others.

Image: myknowledgepower.com
Navigating the Intersection of Ascribed and Achieved Status
The interplay between ascribed and achieved status is complex and multifaceted. While we might strive to achieve a certain social standing, the realities of our ascribed status often influence our journey. A person of color, for instance, may face additional challenges in achieving success compared to someone who benefits from inherent privileges.
Recognizing the interplay between these two forms of status is vital for building a more just and equitable society. It requires acknowledging the systemic inequalities that exist, understanding how they impact individuals and groups, and working toward dismantling the structures that perpetuate them.
Moving Forward: Toward a More Equitable Future
The understanding of ascribed status doesn’t simply offer a lens for analyzing social inequality; it empowers us to take action. Here are some concrete ways we can work towards creating a more just and inclusive society:
-
Empowerment through Education: Educating ourselves and others about the complexities of ascribed status is a vital first step. By fostering awareness and critical thinking, we can challenge discriminatory practices and create a more informed citizenry.
-
Advocacy and Activism: Engage in advocacy and activism by supporting organizations working to address systemic inequalities rooted in ascribed status.
-
Promoting Inclusive Policies: Advocate for policies that dismantle structures of discrimination and promote equality of opportunity regardless of one’s ascribed status.
-
Cultivating Empathy: Foster empathy and understanding for individuals and groups who experience disadvantages due to ascribed status. Listen to their stories, challenge harmful stereotypes, and create spaces for dialogue and collaboration.
Ascribed Status Sociology
A Powerful Reminder
Ascribed status serves as a powerful reminder that our social realities are not determined solely by our individual efforts. It highlights the importance of examining the social structures that shape our lives, acknowledging the influence of systemic inequalities, and working collectively towards a more just and equitable future. By understanding the power of ascribed status, we can create a world where everyone has the opportunity to thrive, regardless of the circumstances of their birth.






