Imagine a bustling city, teeming with people going about their daily lives. Beneath the surface of individual actions lie intricate systems that govern how we interact, work, learn, and worship. These systems are known as social institutions – the fundamental building blocks of our society. They provide order, stability, and a framework for our collective existence. Just like the skeletal system supports our bodies, social institutions provide the structure that holds civilization together. But what exactly are these invisible forces that influence every aspect of our lives?
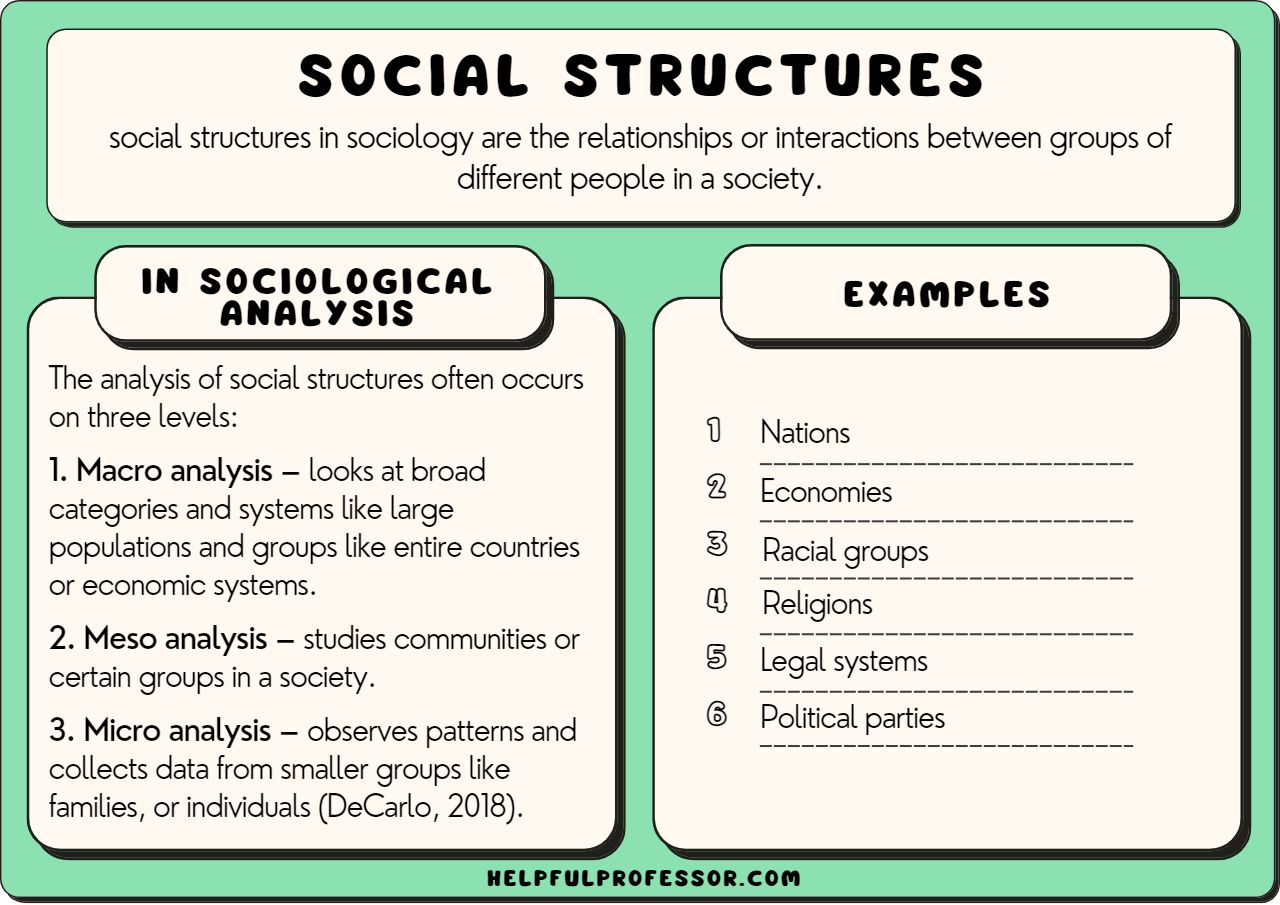
Image: helpfulprofessor.com
Throughout history, we’ve witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the evolution of technology, and the changing dynamics of social interactions. Whether it’s the government shaping laws, schools educating the youth, or religious organizations providing spiritual guidance, social institutions have always played a pivotal role in shaping our world. In this exploration, we’ll delve deeper into the concept of social institutions, uncovering their significance, evolution, and impact on our modern lives.
Defining Social Institutions: The Pillars of Society
A social institution is a complex network of established norms, values, and roles that regulate and guide human behavior in a specific area of social life. These institutions are not static entities; they are dynamic and constantly evolving in response to societal changes. They serve as the foundation upon which our social order is built, providing structure and meaning to our individual and collective experiences.
Think of a social institution like a blueprint for society. Just as a blueprint outlines the structure of a building, a social institution defines the rules, expectations, and practices associated with a particular aspect of social life. For instance, the institution of marriage outlines the norms, roles, and responsibilities associated with this form of union, while the institution of education dictates the processes of knowledge acquisition and dissemination. These institutions are often intertwined, their boundaries blurring as they influence and shape each other.
Types of Social Institutions: A Diverse Landscape
Social institutions cover a broad spectrum, encompassing various areas of human life. Some of the most prominent institutions include:
- The Family: A fundamental institution, responsible for procreation, socialization, and emotional support. It provides the initial foundation for individual growth and development.
- The Economy: The system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It governs how we acquire resources, earn a living, and participate in the market.
- Education: The institution responsible for transmitting knowledge, skills, and values to future generations. It plays a crucial role in shaping individuals’ cognitive abilities and social development.
- Religion: A system of beliefs and practices designed to provide meaning and purpose in life. It offers a framework for understanding the world, connecting with the divine, and guiding ethical behavior.
- Government: The institution responsible for maintaining order, enforcing laws, and providing public services. It governs the political landscape and ensures the functioning of society.
- Healthcare: The institution responsible for preventing, diagnosing, and treating illness. It encompasses a wide range of institutions, including hospitals, clinics, and research centers, focused on maintaining public health.
Understanding the Evolution and Functions of Social Institutions
Social institutions are not static entities, frozen in time. They evolve and adapt over time, reflecting the changing needs and values of society. The family institution, for instance, has undergone significant transformations throughout history, evolving from extended families to nuclear families and, more recently, embracing diverse family structures.
These shifts are driven by various factors, including technological advancements, social movements, and global interconnectedness. Technological innovations, such as the internet and social media, have profoundly impacted how we communicate, access information, and interact with others, shaping the norms and practices associated with various institutions, including family, education, and the economy.
Social institutions serve a vital range of functions that contribute to the stability and functioning of society. These functions include:
- Socialization: Institutions play a role in shaping individuals’ values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors. From learning the basics of language and social skills within families, to acquiring knowledge and values in educational institutions, socialization prepares individuals for their roles in society.
- Social Control: Institutions establish rules, norms, and expectations that guide behavior and ensure order within society. Laws, societal norms, and religious teachings serve as mechanisms to maintain social control and prevent chaos.
- Production and Distribution of Goods and Services: Economic institutions, such as businesses, corporations, and governments, are responsible for the production and distribution of goods and services necessary for sustenance and economic well-being.
- Conflict Resolution: Social institutions, including legal systems and religious organizations, provide mechanisms for resolving conflicts and disputes among individuals and groups.
- Social Integration: Institutions foster a sense of belonging and shared identity by promoting common values, beliefs, and practices. This integration helps to maintain social harmony and prevent fragmentation.
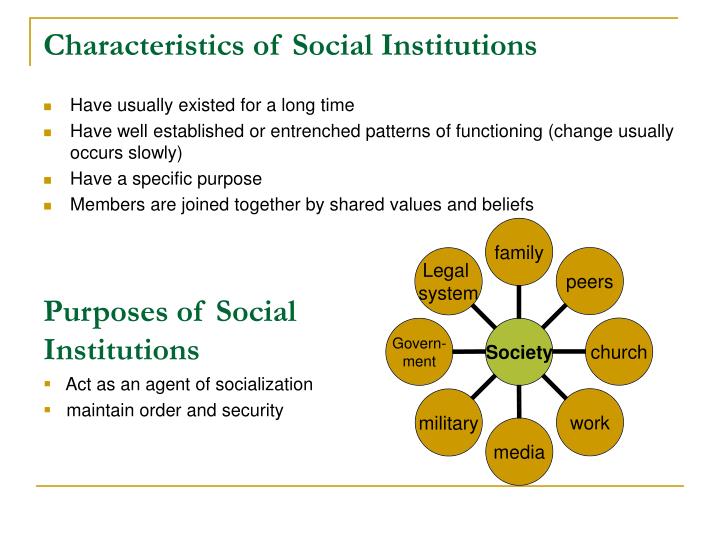
Image: www.slidemake.com
Current Trends and Developments in Social Institutions
The 21st century presents a dynamic landscape where social institutions are continuously adapting to emerging challenges and trends. Here’s a glimpse into some of these developments:
- Globalization and Interconnectedness: Our increasingly interconnected world is fostering new forms of interaction and collaboration across borders. This has profound implications for institutions, leading to the rise of global organizations and the need to address issues with a global perspective. For example, the rise of multinational corporations and international organizations indicates the growing impact of global forces on national institutions.
- Technology and Digital Revolution: Advancements in technology, particularly in the digital sphere, are reshaping how we interact with institutions and each other. Examples include online education, remote work, and social media platforms, which are transforming the norms and practices associated with education, employment, and communication.
- Demographic Shifts and Societal Diversity: Changing demographics, such as aging populations and increasing diversity, force institutions to adapt and become more inclusive. This includes adapting education systems to meet the needs of diverse learners, reforming healthcare systems to cater to aging populations, and promoting policies that recognize and value societal diversity.
- Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: The increasing urgency of environmental issues is influencing how institutions operate and approach sustainability. From promoting green practices in businesses to incorporating environmental education into schools, institutions are evolving to address the challenges of climate change and resource depletion.
Tips and Expert Advice: Navigating the World of Social Institutions
Understanding social institutions is crucial for comprehending and navigating our complex world. Here are some tips to help you navigate this landscape:
- Stay Informed: Be aware of the latest developments and challenges facing social institutions. Engage with news sources, research reports, and discussions that explore issues related to institutions, such as education, healthcare, and the environment. This allows you to gain a deeper understanding of how institutions are evolving and their impact on society.
- Engage Actively: Participate in discussions, share your perspectives, and contribute to shaping the direction of institutions. You can get involved in advocacy groups, local communities, and political processes to make a difference in the areas of social life that are important to you.
- Embrace Diversity: Recognize and respect the diversity of viewpoints and experiences within and across institutions. This involves understanding the perspectives of different individuals and groups, acknowledging their contributions, and working toward inclusive practices that value and benefit everyone.
- Critical Thinking: Question assumptions, challenge conventional wisdom, and consider alternative perspectives. By engaging in critical thinking, you can better understand the underlying dynamics of institutions and their impact on individuals and society.
Navigating the complex world of social institutions requires a combination of knowledge, critical thinking, and active engagement. By staying informed, participating in discussions, embracing diversity, and fostering critical thinking, you can become more aware of the forces that shape our lives and contribute to a more just and equitable society.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a social institution and a social group?
A social institution is a broad, overarching system of norms, values, and roles that govern a specific area of social life, while a social group is a collection of individuals who share common characteristics, goals, or interests. A family is a social group, but the institution of family encompasses the broader societal norms, roles, and expectations associated with family life. Social groups operate within the framework of social institutions.
How can social institutions be reformed or improved?
Social institutions can be reformed or improved through a combination of individual and collective efforts. This involves advocating for policy changes, promoting social movements, engaging in civil discourse, and actively participating in the decision-making processes that shape institutions. It’s important to work collectively, to bring about lasting change.
Do social institutions always benefit society?
While social institutions aim to provide order and stability, they can sometimes perpetuate inequalities and injustices. It’s important to critically examine the impact of institutions and advocate for reforms that ensure fairness, equality, and the well-being of all members of society.
What Is Social Institution
Conclusion
Social institutions are the invisible forces that shape our lives, providing structure, meaning, and a framework for our collective existence. Understanding their functions, evolution, and the challenges they face is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern society. By staying informed, engaging actively, and fostering critical thinking, we can contribute to a more just and equitable society.
Are you interested in learning more about specific social institutions and their impact on your life? What social institutions do you think need the most attention and reform in today’s world?






