Have you ever wondered why you follow certain social norms? Why you feel pressure to conform to certain trends? These are all examples of social controls, the intricate mechanisms that guide our behavior within society. Social controls, like the invisible hand of society, influence our decisions, shape our values, and even tell us how to act in different situations. Imagine walking into a crowded room, and instantly, you know how to behave; whether to speak softly or loudly, whether to stand or sit, whether to engage in conversation or observe. That’s social control at work!

Image: www.slideshare.net
Social controls are not always overt or easily identifiable. Sometimes they exist in subtler forms – a raised eyebrow, a disapproving look, or even just a shared understanding of what’s appropriate. These subtle cues can be just as powerful as more explicit rules and regulations, shaping our actions in a myriad of ways. While social controls can be beneficial, ensuring social order and promoting cooperation, they can also be misused to exert undue influence or suppress individual freedom. Understanding the intricacies of social controls is crucial to navigating a complex world filled with competing social forces.
Understanding Social Control: Its Definition, History, and Meaning
Social control refers to the myriad of ways in which society seeks to regulate the behavior of its members. It is a complex phenomenon involving a combination of formal and informal methods, both explicit rules and implicit expectations. This control can be exerted through various institutions, including family, education, religion, the legal system, and even social media. These mechanisms operate to promote conformity, maintain order, and ensure stability within a society, often by rewarding desired behavior and discouraging deviance.
The concept of social control can be traced back to the early days of sociological thought. Thinkers like Émile Durkheim and Max Weber recognized the importance of social forces in shaping individual behavior. Durkheim, for instance, stressed the shared beliefs, values, and norms that bind individuals together, creating a collective conscience that guides conduct and prevents social chaos. Weber explored the increasing rationalization of society and how bureaucracy played a significant role in controlling behavior through formal rules and regulations.
Today, the study of social control remains a crucial field of inquiry in sociology. Scholars continue to examine the multifaceted ways in which society influences behavior, addressing the nuances of control, the potential for abuse, and the dynamics of social change in the modern era.
Types of Social Control
Social controls operate through a spectrum of methods, encompassing both formal and informal approaches. Formal controls refer to clearly defined rules and regulations enforced by institutions like the government or legal system. These controls often carry consequences for violating established norms, such as fines, imprisonment, or other sanctions. Examples include traffic laws, criminal codes, and school regulations.
Informal controls, on the other hand, are less explicit and operate through social pressure, norms, and expectations. They are often communicated through subtle cues, social sanctions, and shared understandings. These controls rely on the social consequences of non-conformity, such as social disapproval, ostracism, or reputational damage. Examples include societal expectations about politeness, dress codes, or even the unspoken rules of a particular group or community.
Examples of Social Controls
Social controls are woven into the fabric of our everyday lives, influencing our choices in countless ways. Here are some examples:
- Family: Parental rules, family traditions, and expectations about behavior are fundamental forms of social control. They teach us about right and wrong, define acceptable behavior, and shape our values.
- Education: Schools instill values, teach rules, and encourage conformity through curriculums, disciplinary actions, and social interactions with peers.
- Religion: Religious institutions communicate moral codes, ethical guidelines, and social expectations, influencing behavior and shaping beliefs.
- The Legal System: Laws, courts, and law enforcement agencies provide a framework for formal social control, establishing rules, consequences for violations, and mechanisms for dispute resolution.
- Social Media: The digital age has brought about new forms of social control, with online platforms influencing behavior through social pressure, online communities, and digital reputation management.
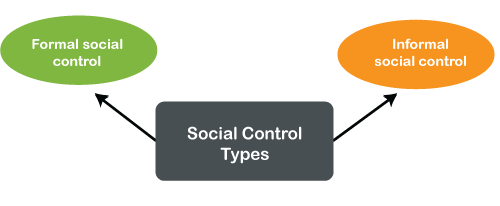
Image: www.tutoraspire.com
Current Trends and Developments in Social Control
The landscape of social control is constantly evolving, driven by rapid social changes, technological advancements, and shifting societal values. Some key trends shaping the contours of social control in the 21st century include:
- The Rise of Digital Social Control: The internet and social media have become powerful tools for regulating behavior. Digital platforms allow for greater surveillance, tracking user activity, and influencing online behavior through algorithms, social pressure, and online reputation management.
- Shifting Power Dynamics: Social movements and protests have challenged traditional structures of social control, demanding greater accountability and justice. This has led to increased scrutiny of institutional power and the need for more equitable and inclusive systems of control.
- The Impact of Globalization: The interconnected nature of the modern world has created new challenges for traditional social controls. Cultural shifts, global migration, and the rise of transnational institutions have introduced complexities and require new approaches to managing behavior across diverse populations.
- Individualism vs. Collective Responsibility: The tension between individual freedom and the need for social order is a constant theme in the discussion of social control. Balancing personal autonomy with the societal need for stability, cooperation, and respect remains a crucial challenge in the 21st century.
Tips for Effective Social Control
Effective social control relies on a delicate balance between promoting conformity and respecting individual autonomy. Here are some tips for navigating the complexities of social controls and fostering positive social outcomes:
- Promote Understanding, Not Just Enforcement: Building a strong sense of community and shared values through education and dialogue fosters a deeper understanding of social norms.
- Emphasize Empathy and Dialogue: Encouraging empathy and open communication helps to address conflict constructively and build understanding among individuals with different perspectives.
- Focus on Prevention and Rehabilitation: Investing in programs that address the root causes of social problems can help prevent deviance and promote positive change.
- Uphold Fairness and Transparency: Ensuring that systems of control are applied fairly and transparently strengthens public trust and legitimacy.
- Embrace Critical Thinking and Open Discussion: Encourage healthy skepticism and informed debate about social norms, challenging assumptions and promoting thoughtful engagement with societal issues.
Expert Advice on Navigating Social Controls
Social controls are a reality of life in any society. Navigating this complex landscape requires a nuanced approach. Here’s expert advice based on research and experience:
Firstly, it is essential to be aware of the various social controls that operate in your life. Recognize how these mechanisms influence your behavior, both consciously and unconsciously. Secondly, cultivate a critical lens that allows you to question assumptions, challenge societal norms, and advocate for positive change. Lastly, engage in open dialogue, respectfully express your views, and build bridges of understanding with others who may hold different perspectives.
FAQs about Social Control
Q: Is social control always negative?
No, social control is not inherently negative. It plays a crucial role in maintaining order, promoting cooperation, and ensuring the well-being of society. While some forms of social control can be oppressive, others are vital for social harmony.
Q: How can I resist harmful social control?
Resisting harmful social control requires awareness, critical thinking, and a willingness to speak out. Educate yourself about the dynamics of power and influence, challenge oppressive norms and ideologies, and advocate for change.
Q: How do I balance my individual freedom with social responsibilities?
Finding the balance between individual freedom and social responsibility is a constant challenge. The key is to seek understanding and find common ground with others. Respecting differing perspectives, engaging in open dialogue, and promoting compromise through ethical and responsible choices are crucial steps toward a harmonious society.
What Are Social Controls
Conclusion
Social controls are a complex and multifaceted aspect of human society. Understanding their various forms, their impact on our lives, and the ethical implications of their application is vital for navigating the complexities of modern life. By promoting critical thinking, advocating for fairness and justice, and fostering inclusive dialogue, we can work towards a more equitable and fulfilling society.
Are you interested in learning more about social controls and how they affect our world? Let us know your thoughts and questions in the comments below!






