As I was learning Spanish, I came across a curious and slightly confusing situation. I was trying to describe a beautiful painting and wanted to use the word “that” in Spanish. But then, a nagging doubt crept in: “Is it eso or esa?” I soon learned that these seemingly simple words held within them the subtle yet crucial distinction of gender in Spanish. This realization sparked my fascination with the nuances of the language.

Image: www.derechoshumanos.gob.ec
Understanding eso and esa goes beyond just knowing the right word to use. It reveals a deep-rooted linguistic system that influences how we communicate and perceive the world around us.
Unraveling the Mystery: Eso and Esa
In Spanish, every noun is assigned a grammatical gender: masculine or feminine. This isn’t about the object itself, but rather a convention that shapes how we speak and write. Eso and esa are demonstrative adjectives (also known as demonstrative pronouns), words that point to a specific noun.
Eso refers to masculine nouns, while esa designates feminine nouns. Think of it as pointing with your finger and saying “that” – but in Spanish, you need to point with the right gendered “finger.”
The Grammar Rules:
To grasp this, let’s look at a few examples:
-
Eso is a beautiful libro (that is a beautiful book – libro is masculine).
-
Esa is a delicious torta (that is a delicious cake – torta is feminine).
-
Eso is a vibrant cielo (that is a vibrant sky – cielo is masculine).
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Significance
While mastering eso and esa may seem like a small step, it opens the door to a deeper understanding of Spanish grammar. This concept extends far beyond just these two words. It impacts everything from adjective agreement to verb conjugation.
For example, if you describe a beautiful casa (house), you would use the feminine adjective hermosa (beautiful). This consistency in gender agreement ensures fluency and elegance in the language.
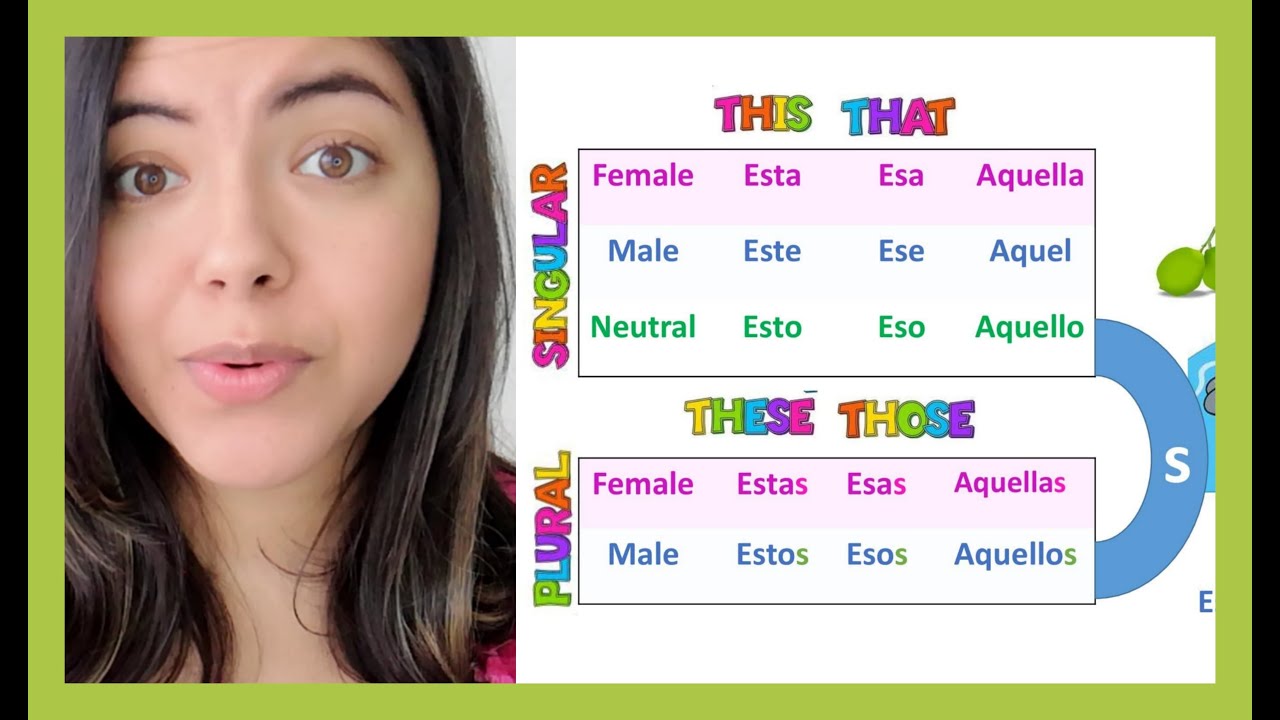
Image: www.youtube.com
Grasping the Nuances:
The concept of gender in Spanish can initially seem a bit confusing, particularly for those coming from languages that don’t have grammatical gender. Here’s a helpful analogy: Think of gender in Spanish as a kind of invisible label attached to every noun. By recognizing those labels, you effectively understand the language’s underlying structure.
Learning these rules isn’t just about memorizing; it’s about recognizing a pattern that guides how Spanish speakers communicate and perceive the world.
Top Tips and Expert Advice: Understanding Eso and Esa
Here are some strategies to help you master the gender game in Spanish:
-
Start with the Basics:
Familiarize yourself with the common gender endings for nouns like –o (masculine), –a (feminine). You can also utilize dictionaries and online resources to double-check the gender of any unfamiliar nouns.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice:
Engaging in conversation, reading Spanish literature, and watching films and TV shows can greatly accelerate your learning. The more you expose yourself to the language, the more intuitive the gender system will become.
-
Embrace the Challenge:
Don’t be discouraged if you make mistakes. Everyone stumbles at first. Pay attention to these errors and try to understand the underlying reason for them. With each correction, you’ll move closer to fluency.
Mastering Spanish Gender:
Understanding gender in Spanish is an ongoing journey. Every encounter with the language, every new word you learn, and each conversation you have, will strengthen your understanding of this fundamental linguistic element. Remember, patience and persistence are key.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between ese and esa?
Ese and esa are similar to eso and esa, but they point to things that are closer to the speaker. Ese refers to masculine nouns that are closer to the speaker, while esa refers to feminine nouns.
2. What are other examples of words that change with gender?
Many adjectives, articles (like “the” and “a”), and even some verbs change their forms in Spanish based on the gender of the noun. For example, “big” is grande for masculine nouns and grande for feminine nouns.
3. Is it okay to make mistakes during language learning?
Absolutely! Making mistakes is a natural part of language acquisition. Embrace your errors as opportunities to learn and improve.
Eso Y Esa
Conclusion:
Eso and esa are more than just words; they represent keys to unlocking a vibrant and nuanced language. By understanding the concept of gender in Spanish, you gain a deeper appreciation for its intricacies and beauty. Are you ready to dive into the world of Spanish grammar and explore its fascinating depths?






