Have you ever found yourself scrolling through a website, downloading a file, or watching a video, only to encounter the terms “gigabit” and “gigabyte” and wonder what they actually mean? These terms can be confusing, especially when they look so similar. In the fast-paced world of technology, where data speeds and storage capacities are constantly expanding, it’s essential to grasp the distinction between these two common units of measurement. Understanding this difference empowers you to make informed decisions about your internet plan, storage needs, and overall digital experience.
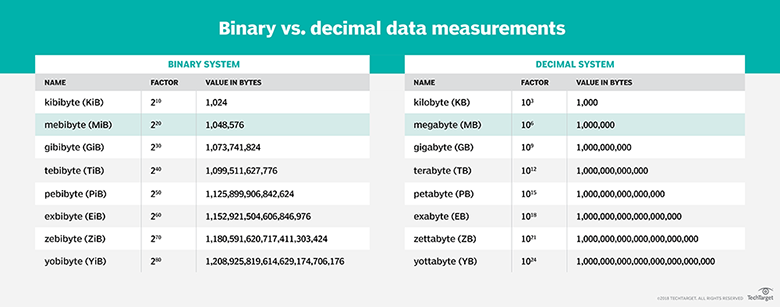
Image: www.sdskpx.com
This article will guide you through the distinction between gigabit and gigabyte, explaining their significance in the digital world. We’ll explore their definitions, uses, and how they relate to your internet speed and file sizes.
Gigabit and Gigabyte: Unveiling the Difference
Gigabit and gigabyte are both units of measurement used in the digital world, but they represent different aspects of data. While both terms are associated with data, they measure distinct elements: speed and size. Imagine a highway with cars representing data. The gigabit would measure the speed of the cars on the highway, while the gigabyte would measure the total size of all the cars on the highway.
Gigabit: Measuring Data Transfer Speed
A gigabit (Gb) measures the speed at which data is transferred. It represents a billion bits of data per second, or 1,000,000,000 bits per second. Think of a gigabit as the velocity of data flowing through a digital pipeline. It’s analogous to a highway’s speed limit; the higher the gigabit rate, the faster information moves. When you choose an internet plan, the advertised speed is often expressed in gigabits per second (Gbps).
Gigabyte: Measuring Data Storage Size
A gigabyte (GB) measures the size of a file or the storage capacity of a device. It represents one billion bytes of data, or 1,000,000,000 bytes. Consider a gigabyte like the size of a container holding data. A video file, an image, or a program takes up a certain amount of space in terms of gigabytes. When you purchase a hard drive, its storage capacity is typically expressed in gigabytes.
Image: www.reichelt.com
The Big Picture: Connecting Gigabit and Gigabyte
Although gigabits and gigabytes are different, they are interlinked. The data speed expressed in gigabits per second determines how quickly files measured in gigabytes can be downloaded or uploaded. A higher gigabit speed enables faster data transfer, allowing you to download large gigabytes files in less time. For instance, if you have a 1 Gbps internet connection, you can download a 1 GB file in about 8 seconds, significantly faster than if you had a 1 Mbps connection.
The Increasing Demand for High-Speed Internet
The digital landscape is rapidly evolving, driving the demand for higher-speed internet connections. Streaming services, online gaming, cloud-based storage, and remote work are just some of the driving forces behind this trend. To effortlessly handle these data-intensive activities, consumers and businesses alike are seeking connections with more gigabits per second. This shift reflects the importance of speed in today’s interconnected world, as people increasingly rely on the internet to access and share information on the go.
Choosing the Right Internet Plan: A Gigabits Perspective
With so many internet plans available, choosing the right one can be perplexing. To make the best decision for your needs, consider the data-intensive activities you engage in regularly and the average number of devices connected to your home network. For instance, if you stream videos in 4K resolution, play online games, or work remotely, a higher gigabits per second plan is recommended for a smooth and seamless experience. However, if your primary internet use involves email, basic web browsing, and social media, a lower-speed plan might suffice.
Tips and Expert Advice: Maximizing Your Data Experience
To enhance your data experience, here are some practical advice to keep in mind:
- Prioritize speed: Invest in an internet plan with sufficient gigabits per second, particularly if you frequently engage in data-heavy activities.
- Optimize storage: Regularly delete unnecessary files to maximize storage space on your devices. Consider cloud-based storage options for backups and to free up space on your local drives.
- Enhance network performance: Ensure your wireless router is properly configured and located in a central position in your home for optimal connectivity.
- Use a wired connection: When possible, connect your devices to your router using an Ethernet cable. This provides a more stable and faster connection compared to Wi-Fi.
Following these tips can help you improve the efficiency and enjoyment of your online journey. Remember, it’s not just about having a fast internet connection but also about using it wisely and optimizing your data experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between megabits and gigabits?
A: A megabit (Mb) is one million bits, while a gigabit (Gb) is one billion bits. So, a gigabit is 1,000 times larger than a megabit. In the context of internet speed, a gigabit connection is significantly faster than a megabit connection.
Q: What is the difference between megabytes and gigabytes?
A: A megabyte (MB) is one million bytes, while a gigabyte (GB) is one billion bytes. So, a gigabyte is 1,000 times larger than a megabyte. When discussing storage space, a gigabyte is a unit used to express the size of a file or the capacity of a hard drive.
Q: How much internet speed do I need?
A: The ideal internet speed depends on your individual needs. If you primarily use the internet for browsing, emailing, and light social media, a slower speed might suffice. However, if you engage in activities like streaming videos, online gaming, or video conferencing, you’ll likely need a faster connection.
Gigabit Or Gigabyte
Conclusion
In the ever-growing digital landscape, the distinction between gigabit and gigabyte is critical to navigate the world of data transfer speeds and storage sizes. Gigabits measure how fast data moves, while gigabytes measure the amount of data. As technology advances, the demand for faster gigabit speeds and larger storage capacities continues to rise. By understanding these fundamental units of measurement, you can make informed decisions about your internet plan, storage needs, and overall digital experience.
Are you interested in learning more about data transfer speeds, storage capacities, or the latest technological advancements?






