The fierce warriors of the steppes, their names echoing through the annals of history, have captivated our imaginations for centuries. The Mongols and Huns, both nomadic peoples renowned for their military prowess and devastating conquests, left an indelible mark on the world. Though separated by time and geography, their stories are intertwined through the common thread of nomadic life and the shared legacy of fear and respect they inspired.
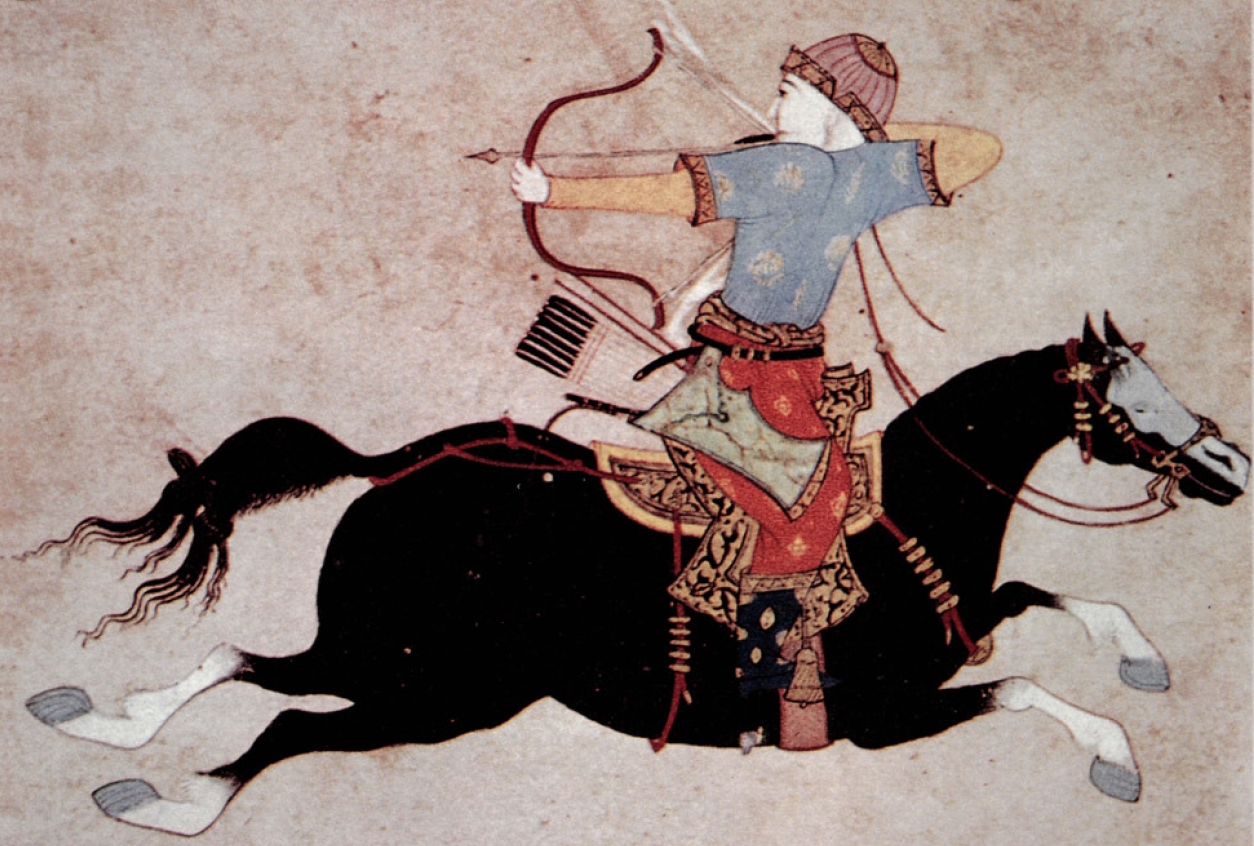

Image: www.history-channel.org
Growing up, I was fascinated by tales of Genghis Khan and Attila the Hun, their names synonymous with power and brutality. I remember poring over maps, tracing their sweeping conquests across vast continents, imagining the clang of their iron swords and the thunder of their horses. This fascination led me to delve deeper into the history of these nomadic empires, understanding the intricacies of their societal structures, military tactics, and the lasting impact they had on the course of human civilization.
The Nomadic Way of Life
A Life on the Move
Both the Mongols and the Huns were nomadic peoples, meaning they lived a life of constant movement. They didn’t cultivate land or build permanent settlements, instead relying on the vast grasslands of Central Asia and Eastern Europe as their home. Their lives were closely tied to the cyclical movements of their livestock, primarily horses and sheep. The Mongols, renowned as skilled horsemen, utilized horses for transportation, hunting, and warfare. The Huns, too, were known for their horsemanship, employing cavalry as their primary fighting force.
Adaptability and Resilience
The nomadic way of life instilled in them remarkable adaptability and resilience. They were accustomed to harsh environments, unpredictable weather, and constant challenges. Their ability to move with the seasons and adapt to new landscapes provided them with a unique edge. This nomadic lifestyle fostered a strong sense of community and a hierarchical social structure, crucial for survival in a constantly changing world. Their reliance on mobility also made them difficult to conquer, as they could retreat into the vast steppes, only to reemerge when the opportunity presented itself.
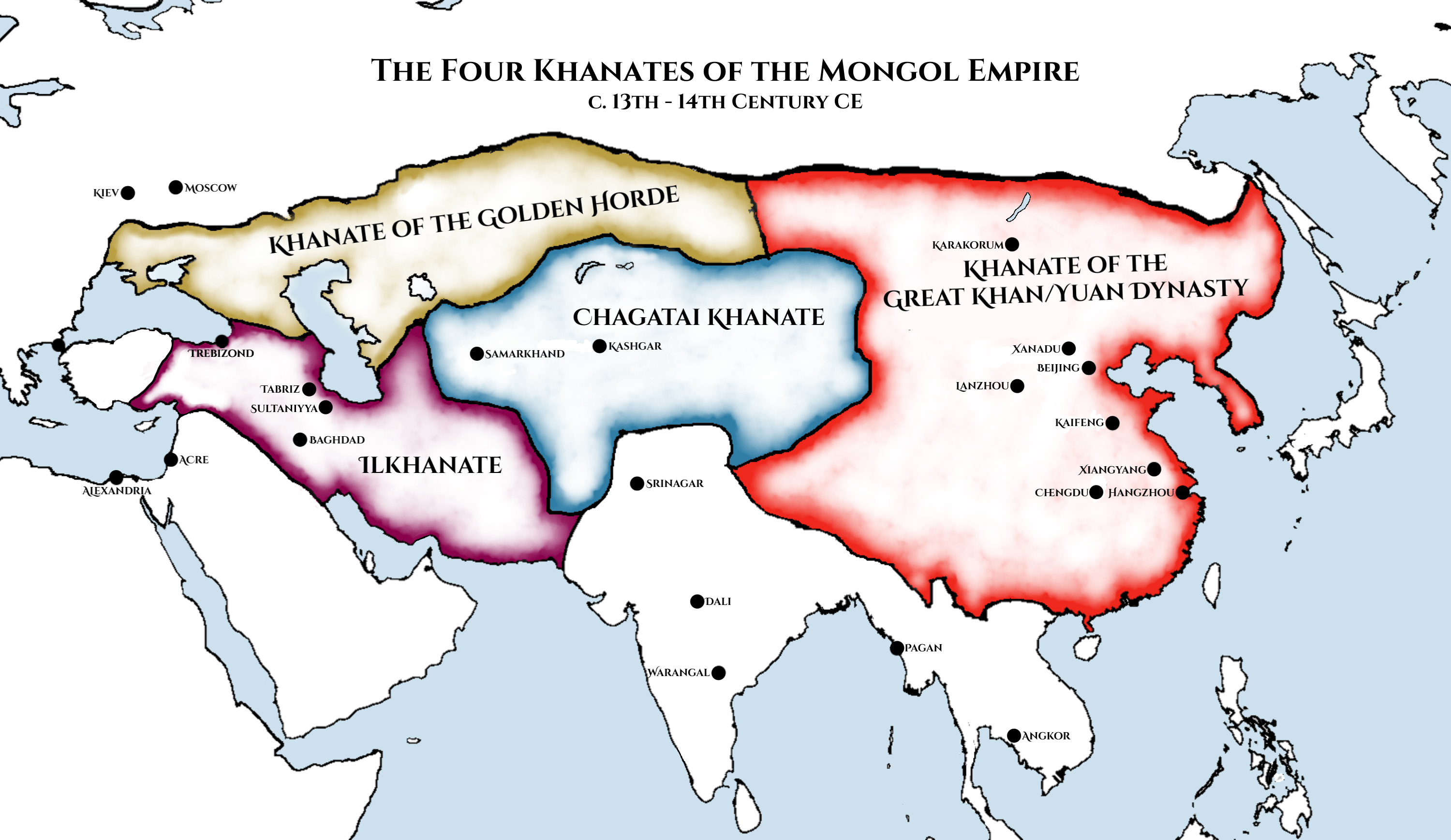
Image: www.vrogue.co
The Rise of the Mongol Empire
Genghis Khan’s Unification
The Mongol Empire, one of the largest empires in history, rose under the leadership of Genghis Khan, a brilliant military strategist and a unifying force. During the 13th century, Genghis Khan consolidated disparate Mongol tribes under his banner, embarking on a series of military campaigns that spread the Mongol Empire from Eastern Europe to the Pacific Ocean. His conquests were marked by ruthless efficiency and a sophisticated understanding of siege warfare and logistics. He employed a highly disciplined and mobile army, adept at utilizing horseback archery and flanking maneuvers, which proved devastatingly effective against the armies of their time.
The Legacy of Pax Mongolica
Despite their brutal conquests, the Mongols also established a period of relative peace and prosperity known as the Pax Mongolica. They maintained a secure trade route network across Eurasia, known as the Silk Road, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange. They also allowed religious freedom within their vast empire, fostering tolerance and interfaith interaction.
The Huns: Terror of the Western Roman Empire
Attila’s Reign of Terror
The Huns, who emerged in the 4th century CE, were known for their fearsome reputation and military tactics. Led by Attila, they launched devastating raids into the Roman Empire, causing widespread panic and destruction. Attila’s military strategies emphasized shock and awe, utilizing their swift and brutal cavalry to outmaneuver their opponents. They were known for their skill in archery and their use of hooked spears, which were particularly effective against Roman infantry.
The Battle of the Catalaunian Plains
The Huns’ greatest challenge came in 451 CE at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, a massive engagement against a coalition of Roman and Visigothic forces. Despite a brutal battle that lasted for hours, Attila’s forces were ultimately forced to retreat, marking a turning point in their campaign of conquest.
The Enduring Legacy
Impact on World History
The Mongols and Huns, though distinct in their strategies and motivations, left a profound legacy on world history. The Mongols, through their vast conquests, established a period of cultural exchange and trade, connecting East and West in ways never before imagined. They also spread their language and customs across a vast swathe of Eurasia, leaving behind lasting cultural influences. The Huns, on the other hand, are remembered for their ferocity and their disruptive role in late Roman history. Their relentless raids played a significant role in weakening the Western Roman Empire, contributing to its eventual fall.
Understanding the Past
Understanding the Mongols and Huns provides a glimpse into the history of nomadic peoples and their influence on the shaping of civilizations. Their strategies, adaptability, and resilience offer valuable lessons in leadership, military tactics, and the importance of cultural exchange. Moreover, their stories serve as a reminder of the cyclical nature of conquest and the enduring impact of human ambition on the world.
Tips for Studying Nomadic Empires
If you’re interested in learning more about the Mongols and Huns, here are a few tips for your research:
- Focus on primary sources: Whenever possible, delve into accounts written by people who lived during the time of the Mongols and Huns, such as the writings of Marco Polo or accounts from Roman historians.
- Explore different perspectives: Don’t just focus on European perspectives. Look at historical accounts from the East, particularly Chinese and Persian writings, which provide valuable insights into the Mongol Empire.
- Learn about the nomadic way of life: Gain an understanding of the social structures, customs, and beliefs of nomadic peoples to better grasp their motivations and strategies.
- Engage with visual resources: Explore maps, artwork, and archaeological evidence to bring the history of these empires to life.
By utilizing these tips, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of the Mongols and Huns, exploring not only their military exploits but also their cultural, social, and economic impact on the world.
FAQs
Q: What were the main differences between the Mongols and the Huns?
A: The Mongols were generally more centralized and politically stable compared to the Huns. The Mongol Empire, under Genghis Khan and his successors, had a clear system of governance and a vast network of trade routes, while the Huns were more fragmented and focused on raiding and plunder.
Q: Did the Mongols always fight with brutality?
A: While the Mongols were known for their military prowess and ruthlessness, they also established a period of relative peace and prosperity, known as the Pax Mongolica, during which trade flourished, and cultural exchange was encouraged.
Q: Where can I find more information about the Mongols and Huns?
A: University libraries, historical societies, and online resources like the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History and the British Museum offer a wealth of information on the Mongols and Huns.
Mongols And Huns
Conclusion
The Mongols and Huns, two nomadic empires that rose and fell, left an indelible mark on the world. Their stories offer a valuable glimpse into the history of nomadic peoples, their strategies, their impact on civilization, and the enduring legacy of their conquests.
Are you interested in learning more about the Mongols and Huns? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!






