Have you ever found yourself baffled by the seemingly endless alphabet soup of technological terms? You’re not alone. In the world of data, two terms that often cause confusion are gigabit and gigabyte. While these words might sound similar, they represent fundamentally different concepts. Understanding the distinction is crucial, especially as we navigate ever-increasing data demands in our digital lives.
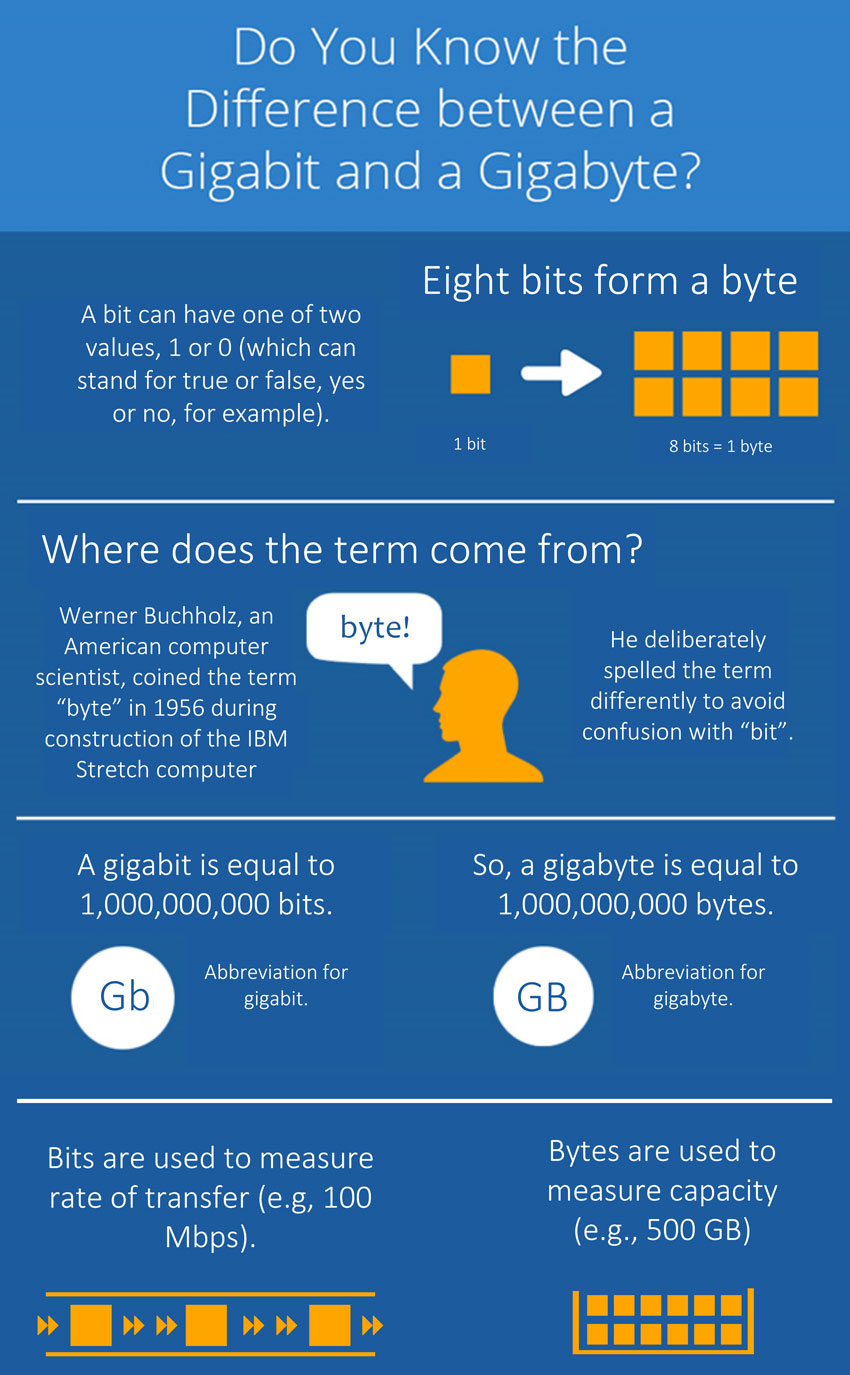
Image: www.atlantic.net
Gigabit and gigabyte, both used to measure data, are often mistaken for each other. However, one measures the speed of data transfer while the other measures the amount of data stored. This article will dissect the differences between these two crucial terms, offering a clear understanding of how they function and why understanding the difference is paramount in today’s digital world.
Digging Deeper: Unveiling Gigabit
Imagine a highway with various lanes. The number of lanes represents the bandwidth, determining the amount of traffic that can pass through at a given time. Gigabit (Gb) is like the number of lanes on this data highway. It quantifies the speed at which data can transfer over a network connection.
Illustrative Example:
Think of downloading a movie. A gigabit connection allows for a rapid download, getting you to the action faster. But even if the movie is small, a slower connection measured in megabits (Mb) will take considerably longer.
Different Gigabit Values:
Gigabit has variations like:
- Gigabit Ethernet: A network standard that delivers data at a speed of 1,000,000,000 bits per second.
- Gigabit Wi-Fi: Wireless networks that use gigabit speeds, offering faster internet browsing and streaming experiences.

Image: candid.technology
Understanding Gigabyte: The Data Storage Unit
Now, shift your focus from the speed of the highway to the capacity of the luggage it carries. Gigabyte (GB) represents the amount of data that can be stored in a digital space. Essentially, it’s a unit of storage capacity.
Practical Uses of Gigabyte:
From our smartphones to our laptops, the most common applications of gigabyte include:
- Hard Drives: Measured in gigabytes, they store your operating system, applications, and personal files.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): Faster and smaller than hard drives, SSDs are also measured in gigabytes, offering quick boot times and enhanced performance.
- Memory Cards: Used in cameras, smartphones, and other devices, memory cards store images, videos, and other data.
- USB Drives: These portable storage devices, also measured in gigabytes, allow you to transfer files between different devices.
The Link Between Gigabit and Gigabyte
While gigabit and gigabyte measure different aspects of data, they are connected. The speed of your internet connection (measured in gigabit) affects how quickly you can transfer or download data (measured in gigabyte). A faster connection allows you to download larger files, like high-definition movies or games, in a shorter time.
Illustrative Example:
Let’s say you have a 1 GB movie file you want to download. With a 1 Gigabit connection, the download will happen faster than with a 100 Megabit (Mb) connection. The gigabit speed lets you transfer the same amount of data (gigabyte) quicker.
A Visual Analogy: Data Streams and Containers
Here’s a straightforward analogy to further clarify the difference. Imagine a fire hose (representing a network connection). The width of the fire hose (gigabit) determines how much water (data) can flow through it per second. The size of the bucket (gigabyte) represents the amount of water (data) you can store.
A wider fire hose (higher gigabit connection) will fill the bucket (download data) faster than a narrower hose (lower gigabit connection).
Real-World Impact of Gigabit and Gigabyte: The Digital Age
Understanding the difference between gigabit and gigabyte is crucial for navigating the digital world. As data consumption continues to increase, a faster internet connection (measured in gigabit) becomes increasingly important for tasks like:
- Streaming High-Definition Video: Enjoy smooth and uninterrupted streaming of movies and TV shows with a gigabit connection.
- Downloading Large Files: Games, software, or high-resolution photos can download in minutes instead of hours.
- Online Gaming: Reduce lag and enjoy a smoother online gaming experience with faster connection speeds.
- Cloud Storage: Back up important files and access them quickly with a high-bandwidth connection.
- Working From Home: Collaborate with colleagues, participate in video calls, and get work done seamlessly with a gigabit connection.
The Future of Data Transfer and Storage: Beyond Gigabit & Gigabyte
The world of data is constantly evolving. As we move towards 5G and beyond, the speeds and storage capacity will continue to increase. While gigabit and gigabyte remain essential units of measurement for now, new terms and technologies will likely emerge.
Trends to Watch:
- Multi-Gigabit Ethernet: Network standards like 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet offer significantly higher speeds, paving the way for faster data transmission.
- Terabyte and Petabyte: As data storage requirements grow, we will encounter larger units like terabyte (TB) and petabyte (PB), representing thousands and millions of gigabytes, respectively.
Difference Between Gigabit And Gigabyte
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Landscape with Understanding
Having a firm grasp of gigabit and gigabyte is essential as we move further into the digital age. To put it simply, gigabit indicates the speed of data transfer, while gigabyte refers to the amount of data stored. Understanding this distinction empowers you to make informed decisions about internet plans, storage devices, and even the way you interact with technology.
As technology continues to evolve, a deeper understanding of these fundamental concepts will only become more crucial. So next time you encounter these terms, remember their distinct roles in the digital world.






