Have you ever wondered what happens inside your spine when you experience a sudden, sharp pain in your back? While the human spine is a marvel of engineering, it’s also susceptible to various conditions, one of which is a “bilobed disc bulge.” This seemingly complex term describes a very specific and often uncomfortable spinal issue, with implications that can significantly impact a person’s life. Understanding what a bilobed disc bulge is, the specific causes, and potential treatment options is critical to managing back pain and achieving optimal spinal health.
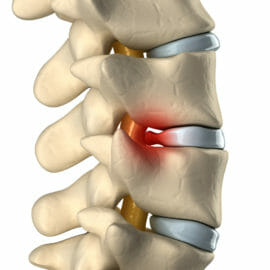
Image: drtonymork.com
This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of the bilobed disc bulge, exploring its anatomical origins, the underlying mechanisms that contribute to its development, and the various strategies employed for management and treatment. We’ll unravel the mystery of this spinal condition and equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your back health.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Your Spine
To grasp the concept of a bilobed disc bulge, we need to first understand the intricate structure of our spine. Imagine a stack of building blocks, each representing a vertebra, forming the bony framework of our back. These vertebrae are interconnected by intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers and facilitate flexible movement. The discs consist of two primary components: the tough outer annulus fibrosus and the gel-like inner nucleus pulposus.
What Exactly is a Bilobed Disc Bulge?
A bilobed disc bulge, also known as a “two-lobed disc bulge,” occurs when the outer ring of the intervertebral disc, the annulus fibrosus, weakens and bulges outward in a distinctive two-lobed shape. This protrusion can press on the surrounding nerves, leading to a range of symptoms, from discomfort and stiffness to debilitating pain and neurological issues.
Unveiling the Causes: Why Does This Happen?
Understanding the causes of a bilobed disc bulge is crucial for effective management and, potentially, prevention. Several factors can contribute to the weakening and bulging of the intervertebral disc, including:
- Age-Related Degeneration: As we age, the discs naturally lose water content, becoming more susceptible to tears and bulges.
- Trauma or Injury: A single forceful impact, like a fall or car accident, can damage the disc and lead to a bulge.
- Repetitive Stress: Performing the same motions repeatedly, such as lifting heavy objects or engaging in certain sports, can cause wear and tear on the discs, eventually leading to a bilobed bulge.
- Poor Posture: Chronic slouching or poor body mechanics can put undue pressure on the spine, contributing to disc degeneration and bulging.
- Genetics: Certain genes can predispose individuals to weaker discs, making them more vulnerable to disc bulges.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts increased pressure on the spine, accelerating the deterioration of the intervertebral discs.

Image: www.neurosurgery-blog.com
Recognizing the Symptoms: Knowing When to Seek Help
The symptoms of a bilobed disc bulge can vary significantly depending on the severity of the bulge and the location of the affected disc. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Back Pain: Sharp, shooting, or aching pain in the lower back, often worsened by movement or prolonged sitting.
- Radicular Pain: Pain that radiates down the leg or arm, following the path of a nerve root. This is frequently described as sciatica or radiculopathy, depending on the affected nerve.
- Numbness and Tingling: A loss of sensation or a tingling sensation in the affected area, particularly in the leg or arm.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the leg or arm, potentially leading to difficulty with balance or coordination.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty bending, twisting, or straightening the back due to pain or stiffness.
Diagnosis: Unraveling the Mystery
A thorough diagnosis is essential for determining the exact cause of your back pain and guiding treatment decisions. A medical professional will typically use a combination of tests to identify a bilobed disc bulge, including:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will assess your range of motion, muscle strength, reflexes, and neurological function to evaluate the extent of symptoms.
- Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: While X-rays can show bony structures of the spine, they may not always reveal a disc bulge.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is the gold standard for imaging soft tissues, providing detailed images of the intervertebral discs and surrounding structures, allowing for definitive identification of a bilobed disc bulge.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans can create detailed cross-sectional images of the spine, particularly useful for evaluating bone structure and any potential nerve impingement from a bulging disc.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests measure the speed and strength of nerve impulses, helping to identify any nerve compression or damage due to the bilobed disc bulge.
Treatment Strategies: Managing the Bulging Disc
The goal of treatment for a bilobed disc bulge is to alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent further damage to the spine. A comprehensive approach often involves various strategies, tailored to the individual patient’s needs and severity of symptoms:
- Conservative Treatment: Most cases of bilobed disc bulge can be managed conservatively, focusing on non-invasive therapies aimed at relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring function.
- Rest: Avoid activities that exacerbate pain and allow the disc to heal.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Apply ice packs for 20 minutes at a time several times a day to reduce inflammation and pain. Heat therapy can be helpful for muscle spasms and stiffness.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen back muscles, improve posture, and increase flexibility. They can also provide guidance on proper lifting techniques and ergonomic principles.
- Epidural Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections into the epidural space around the spinal nerves can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgical Treatment: Surgery is typically reserved for cases where conservative treatment fails to provide adequate relief or when there is significant nerve compression or damage. Surgical options include:
- Discectomy: This procedure removes the bulging portion of the disc, relieving pressure on the nerve root.
- Fusion: This involves joining two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine, often used when a disc bulge affects multiple segments.
- Laminectomy: A portion of the bone covering the spinal canal is removed to create more space for the nerve roots, often used in conjunction with discectomy.
Living with a Bilobed Disc Bulge: The Journey to Recovery
Managing a bilobed disc bulge requires a holistic approach, involving not only medical treatment but also lifestyle modifications to improve overall spinal health.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts stress on the spine, increasing the risk of further disc degeneration. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce pressure on the back.
- Ergonomics: Pay attention to your posture and work habits. Use proper lifting techniques, avoid prolonged sitting, and ensure your desk setup supports good posture.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active can strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and support disc health. Talk to your doctor or physical therapist to create a personalized exercise plan.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate back pain. Techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to the spine and slows down healing, increasing the risk of further disc damage.
Bilobed Disc Bulge: A Look Towards the Future
Medical research continues to explore more advanced non-invasive therapies for treating bilobed disc bulge, focusing on regenerative medicine and minimally invasive techniques. Stem cell therapy, which involves injecting stem cells into the affected disc, shows promise in stimulating disc regeneration and reducing pain. Furthermore, research into minimally invasive procedures, such as laser treatment or radiofrequency ablation, aims to target the bulging disc with less disruption to surrounding tissues.
Bilobed Disc Bulge
The Importance of Proactive Care
While a bilobed disc bulge can be a challenging condition, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you experience any back pain, especially if it persists, radiates down a leg or arm, or is accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness. A proactive approach to managing your spinal health can ensure optimal well-being and prevent debilitating pain.






