Imagine waking up one morning with a nagging pain in your lower back that seems to radiate down your leg. You might struggle to bend over, walk, or even sit comfortably. This discomfort could be the result of a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level, a common condition affecting many individuals. It’s a condition that can disrupt daily life, but understanding its nature and available treatments is crucial for navigating the journey to relief.

Image: yodack.com
A broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc protrudes outward, putting pressure on the surrounding nerves. This pressure can lead to various symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. The L4-L5 segment is particularly vulnerable as it bears significant weight and is subjected to considerable movement during daily activities. Knowing how this condition develops and the options available for treatment can empower you to make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding the Anatomy and Cause
The L4-L5 Disc: A Vital Component
Our spines are made up of 33 individual bones called vertebrae, separated by intervertebral discs. These discs act as cushions and shock absorbers, allowing for flexibility and movement. The L4-L5 disc, located in the lower back, is one of the largest and most susceptible to injury. The disc consists of two parts: the outer annulus fibrosus, a tough fibrous ring, and the inner nucleus pulposus, a gel-like center.
The Formation of a Bulge: A Breakdown in Support
A broad-based disc bulge occurs when the annulus fibrosus weakens or tears, allowing the nucleus pulposus to push outward, creating a bulge. This bulge can press on the nerve roots that exit the spinal canal, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness. The most common causes of disc bulges include:
- Age-related degeneration: Over time, the discs naturally lose water content and become less flexible, making them more prone to bulging.
- Repetitive strain: Activities involving heavy lifting, repetitive bending, or twisting can put excessive stress on the spine, increasing the risk of disc bulges.
- Trauma: Accidents or falls can result in sudden and forceful movements that damage the discs.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a predisposition to disc degeneration due to family history.
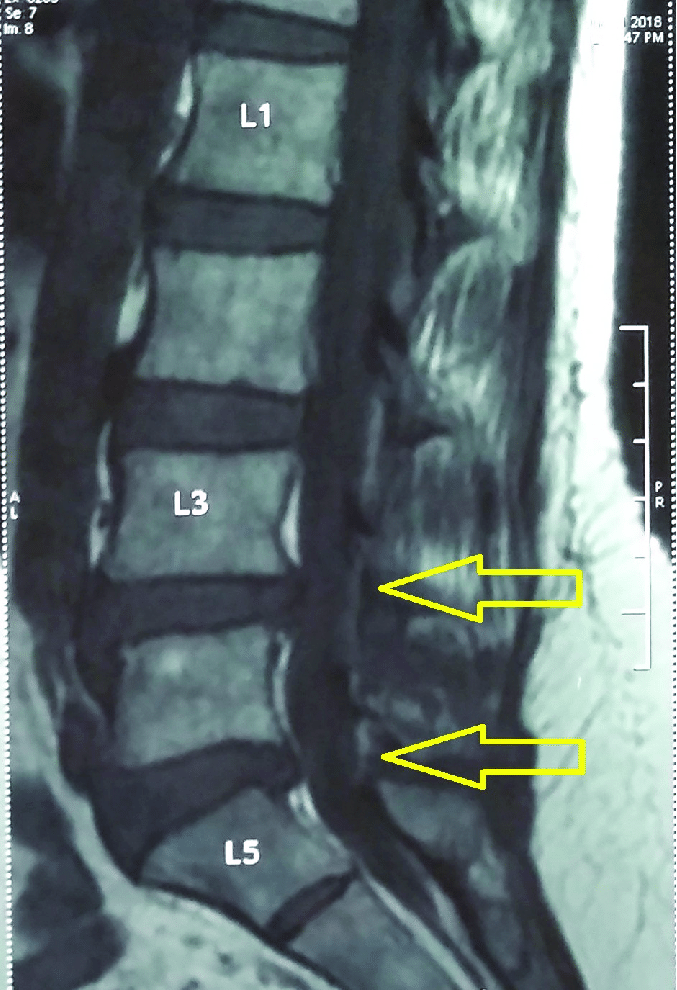
Image: www.researchgate.net
Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs of a Disc Bulge
The symptoms of a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level can vary depending on the severity of the bulge and the degree of nerve compression. Common symptoms include:
- Lower back pain: Often described as a dull ache or sharp pain that worsens with movement.
- Sciatica: Pain that radiates down the leg, typically along the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back to the foot.
- Numbness or tingling: A sensation of pins and needles or numbness in the foot, calf, or even thigh.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting the foot or toes, or a feeling of weakness in the leg.
- Leg pain: Can be felt in the buttocks, thigh, calf, or foot, depending on the location of the nerve compression.
Diagnosis: Identifying the Root Cause
Diagnosing a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level typically involves a combination of:
- Physical examination: A doctor will evaluate your medical history, examine your spine for tenderness, and test your reflexes, strength, and sensation.
- Imaging tests:
- X-rays: Can reveal any abnormalities in the spine, such as a narrowing of the spinal canal.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including the discs and nerves, to confirm the presence and extent of the bulge.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests measure the electrical activity in muscles and nerves to assess the severity of nerve compression.
Treatment: A Multifaceted Approach
The treatment for a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level aims to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further damage. The specific approach may vary depending on the severity of symptoms and individual needs. Common treatment options include:
Non-Surgical Management
- Conservative therapy: Often the first line of treatment, conservative therapy focuses on reducing pain and inflammation using:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen, or stronger prescription medications to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and improve posture.
- Rest: Avoiding activities that worsen pain and reducing pressure on the spine.
- Hot or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Epidural steroid injections: These injections deliver corticosteroids directly to the inflamed nerve roots, providing temporary pain relief and reduced inflammation.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery for a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level is typically considered when conservative measures have not provided adequate relief or when there is significant nerve compression. Common surgical procedures include:
- Discectomy: Involves removing the portion of the disc that is pressing on the nerve. This procedure can be performed through a minimally invasive approach, reducing the risk of complications.
- Laminectomy: Removal of a small portion of the bone on the back of the vertebrae (lamina) to create more space for the nerves.
Rehabilitation: Restoring Function and Preventing Recurrence
Rehabilitation after treatment, whether surgical or non-surgical, is essential for achieving optimal recovery and preventing future episodes. Rehabilitation typically includes:
- Physical therapy: A customized program of exercises to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and develop proper posture.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making changes to daily routines, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding activities that worsen pain, and using proper lifting techniques.
- Pain management: Ongoing pain management strategies to address any residual pain or discomfort.
Living with a Broad-Based Disc Bulge: Managing the Challenges
While a broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level can be a challenging condition, there are strategies for managing the symptoms and living a fulfilling life. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put added strain on the spine.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Strengthening the back muscles and improving flexibility can help prevent future episodes.
- Practicing good posture: Proper posture can reduce strain on the spine and minimize pain.
- Stress management: Stress can worsen back pain. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can be helpful.
- Alternative therapies: Some individuals find relief from acupuncture, chiropractic care, or massage therapy.
Broad Based Disc Bulge L4 L5 Treatment
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Pain Relief
A broad-based disc bulge at the L4-L5 level can be a source of discomfort and disruption to daily life, but it doesn’t have to define your journey. Understanding the condition, exploring treatment options, and embracing a proactive approach to managing symptoms can empower you to regain control over your health.
Remember, an informed and collaborative approach with your healthcare provider is crucial for achieving lasting pain relief and optimal quality of life.
If you’re experiencing lower back pain or sciatica, it’s essential to consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. By working together, you can navigate the challenges of a broad-based disc bulge and find relief from pain.






